-
 Space-time
Space-time
-
 DCE
DCE
-
 Akinesia
Akinesia
-
 Imidazoles
Imidazoles
-
 Newtonian mechanics
Newtonian mechanics
-
 Axial skeleton
Axial skeleton
-
 Folliculitis
Folliculitis
-
 Germ
Germ
-
 Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
-
 Juvenile
Juvenile
-
 Mesoderm
Mesoderm
-
 Planck length
Planck length
-
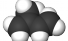 Isoprene
Isoprene
-
 Mammography
Mammography
-
 Asymmetric cryptography
Asymmetric cryptography
-
 NASA
NASA
-
 Hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzine
-
 SOHO
SOHO
-
 Metallicity
Metallicity
-
 Conductivity
Conductivity
-
 Special conservation zone
Special conservation zone
-
 Coprostanol
Coprostanol
-
 Female condom
Female condom
-
 Bomb
Bomb
-
 Bone
Bone
-
 Gametangium
Gametangium
-
 ADSL
ADSL
-
 Photoperiod
Photoperiod
-
 Apothecary
Apothecary
-
 Urine M&C
Urine M&C
Fallow deer
Fallow deer (Linnaeus 1758) - Dama dama
- Order: Artiodactyla
- Family: Cervidae
- Subfamily: Cervinae
- Genus: Dama
- Size: 1.40 to 1.60 m (height at withers 0.80 to 0.95 m)
- Weight: 45 to 70 kg
- Life span: 16 years
IUCN conservation status: LC least concern
Description of the fallow deer
The fallow deer is a cervid with flat, webbed antlers which are shed every year. Its coat is usually tawny or reddish with white spotted patches. Its coat is usually tawny or reddish with white spotted patches.Its underside and slender, delicate legs are cream to whitish. In winter its coat is brown. Its tail, which is small and in constant movement, marks the centre of a white rump patch bordered by black lines. The large, strong neck bears a delicate, cone-shaped head. Facial glands are visible under each eye.The deer has exceptional diurnal vision.

Fallow deer. © Patrick Straub
Habitat of the fallow deer
The fallow deer originates from east of the Mediterranean basin, but was naturalised since ancient times throughout Southern Europe and the Middle East. The major wild or feral herds resulting from releases in the Middle Ages are currently found in Central Europe, while escapees from parks have recently formed forest populations in France. Dama mesopotamica is a similar species and has withdrawn to the forests of southern Iraq and Iran. Sparse forests of broad-leaved trees and meadows are this deer's usual biotope.
Herd of fallow deer. © 4028mdk09, CCA-S A 3.0 Unported license
Behaviour of the fallow deer
For most of the year both sexes of the animal live separately and only come together during the rutting season. Herds generally consist of about a dozen doe and yearling fawns, while males live alone or in small groups. The fallow deer is the most nervous, but, paradoxically, also the most curious deer. When it is alarmed it tries to hide in the undergrowth of dense forests of tall trees. Its territory covers a quite limited area in which it lives in accordance with its needs. It remains under cover during the day and rests, and leaves the undergrowth at dusk until dawn to graze.
Reproduction of the fallow deer
During the rut which begins in early October and lasts until early November, the male's facial glands secrete an oily, thick, black substance. The belling, which is quite unpleasant, looks like a sort of vomiting. The female gives birth, to one or sometimes two fawns, in early summer after a gestation period of about eight months. The female nurses her young for a few months and sexual maturity is reached after about sixteen months. The does, however, are only able to procreate at the end of their second year.

Fawn. © Ciwi, GNU FDL Version 1.2
Diet of the fallow deer
The fallow deer is a ruminant herbivore which mainly feeds on grass, but also eats fruit such as acorns, chestnuts and berries. It is very fond of the bark of ash trees which it gnaws thanks to the angle of its incisors. But its menu also includes buds, leaves and young branches.
Threats to the fallow deer
As opposed to its cousin the Persian deer, which is classified EN (endangered) by the IUCN, the European fallow deer is not considered to be a threatened species.
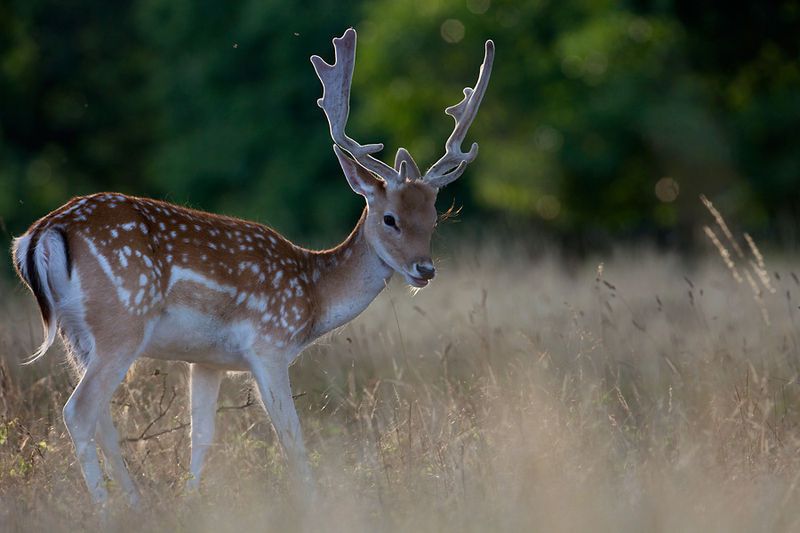 Photo of a fallow deer. © Marek Szczepanek, GNU FDL Version 1.2
Photo of a fallow deer. © Marek Szczepanek, GNU FDL Version 1.2
Latest
Fill out my online form.




