-
 Benthic
Benthic
-
 Subfertility
Subfertility
-
 Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis
-
 Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis
-
 International Nuclear Event Scale
International Nuclear Event Scale
-
 Gene
Gene
-
 Polyp
Polyp
-
 CA
CA
-
 Blood-brain
Blood-brain
-
 Subspecies
Subspecies
-
 Detoxification
Detoxification
-
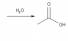 Hydrolase
Hydrolase
-
 Goldschmidt classification
Goldschmidt classification
-
 Condensation
Condensation
-
 Autonomous
Autonomous
-
 Pyroxenite
Pyroxenite
-
 Peak oil
Peak oil
-
 Skarn
Skarn
-
 Laparotomy
Laparotomy
-
 Wood pellets
Wood pellets
-
 Metallicity
Metallicity
-
 Extrasystole
Extrasystole
-
 Island arc
Island arc
-
 Segregation
Segregation
-
 Vaccine
Vaccine
-
 DRM
DRM
-
 Pistil
Pistil
-
 Dunite
Dunite
-
 Temperate forest
Temperate forest
-
 Green bean
Green bean
Fish farming
Fish farming is one of the branches of aquaculture. Specialised in raising fish, fish farming can be fresh water or sea water, in permanent enclosures (pools) or in floating cages.
Principle of fish farming
Currently, fish farming techniques for over twenty species have been mastered. These species include sea bream, turbot, salmon, sturgeon (for caviar)...
Other species, such as tuna, are not actually farmed, but fattened. In fact, the techniques for controlling the reproduction of these species have not been mastered. Wild specimens are therefore captured in the open sea and then rounded up in cages to be fattened before actually being fished.
Fish farming is an old technique that was much used in the Middle Ages to provide fish for monks and the European population on Good Friday.
Currently, fish farming is seen as one solution for meeting the high consumer demand for fish, while avoiding over-fishing and the exhaustion of halieutic resources.
Disadvantages of fish farming
However, fish farming presents, like all types of intensive farming, has a certain number of disadvantages: increased development of pathologies, pollution (concentration of excrement, pathogens, veterinary products, etc.), escape of individuals (invasive species, genetic pollution)...
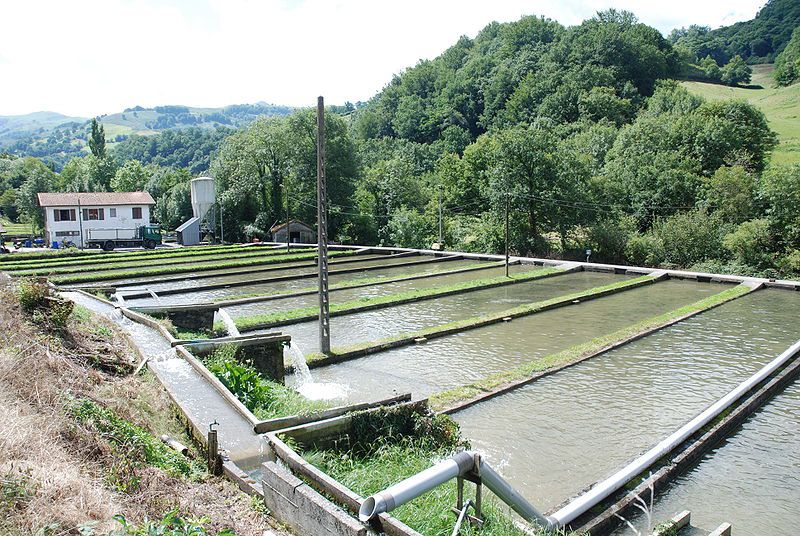 Fish farming ponds in a fresh water fish farm. © Harrieta171, Wikimedia CC by-sa 3.0
Fish farming ponds in a fresh water fish farm. © Harrieta171, Wikimedia CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



