-
 EES
EES
-
 Geosynchronous orbit
Geosynchronous orbit
-
 Reproductive success
Reproductive success
-
 Axial
Axial
-
 Rate-limiting enzyme
Rate-limiting enzyme
-
 Scanner
Scanner
-
 Argos
Argos
-
 Mycorrhizas
Mycorrhizas
-
 Smallpox virus
Smallpox virus
-
 Lava dome
Lava dome
-
 Unbounded universe
Unbounded universe
-
 Crystalline schist
Crystalline schist
-
 Dopamine
Dopamine
-
 Coryza
Coryza
-
 Over-packaging
Over-packaging
-
 Conveyor belt
Conveyor belt
-
 Germinal layer
Germinal layer
-
 Final assembly building
Final assembly building
-
 Skipjack
Skipjack
-
 Flocculation
Flocculation
-
 Primary colour
Primary colour
-
 Creep
Creep
-
 Spreadsheet
Spreadsheet
-
 Liver function test
Liver function test
-
 Heliography
Heliography
-
 Blende
Blende
-
 Air braking
Air braking
-
 VLPO nucleus
VLPO nucleus
-
 Thrombocyte
Thrombocyte
-
 CFM
CFM
Ecomobility
Ecomobility, or sustainable mobility, is a policy for developing and managing local areas and cities that supports practical, low pollution, environmentally friendly mobility, as well as the living environment.
Fields of ecomobility
Sustainable mobility concerns town planning, infrastructure and the organisation of the transport network, as well as technological applications or even awareness raising and education of the population.
Ecomobility rests therefore on the application and development of organisational principles and technologies that favour alternative, 'soft' forms of mobility (walking, bike), public transport and the reduction of pollutants and greenhouse gas emissions.
Ecomobility actions
In concrete terms, ecomobility entails, amongst other actions:
- concentration of an urban space with mixed activities;
- construction of tramways, cycle paths, smart networks, electricity charging terminals…;
- streamlining public transport and making it more reliable;
- encouraging mixed-mode travel (train, tramway, vehicle, bike, etc.);
- implementation of urban mobility plans and business mobility plans;
- increase of clean vehicle fleet (electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, biofuel…);
- awareness raising and education of the population (fuel efficient driving, sharing the road, etc.).
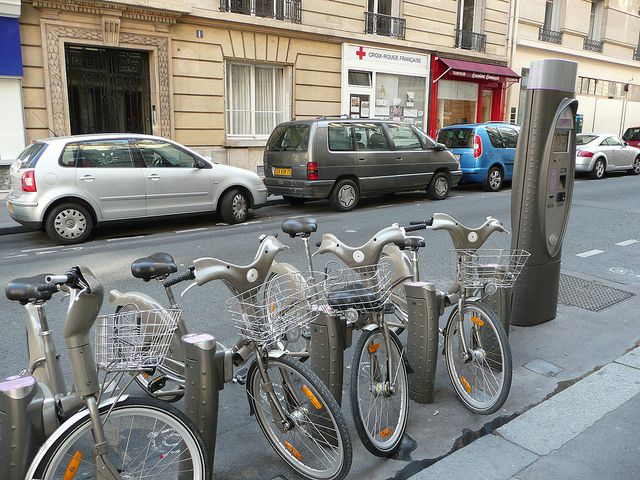 An example of ecomobility: the Vélib system and its infrastructure in the city of Paris. © Grégoire Macqueron CC by-nc-sa 2.0
An example of ecomobility: the Vélib system and its infrastructure in the city of Paris. © Grégoire Macqueron CC by-nc-sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



