-
 Avian influenza
Avian influenza
-
 LHC
LHC
-
 Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhoea
-
 Covalent bond
Covalent bond
-
 Incretin modulators
Incretin modulators
-
 Microgranular rock
Microgranular rock
-
 Solid state laser
Solid state laser
-
 Electric field
Electric field
-
 Nuptial plumage
Nuptial plumage
-
 Galactic coordinate
Galactic coordinate
-
 Tabular facies
Tabular facies
-
 Leonids
Leonids
-
 Pandiculation
Pandiculation
-
 Invertebrate
Invertebrate
-
 Ocean planet
Ocean planet
-
 Amblyopia
Amblyopia
-
 Leucine
Leucine
-
 Essential amino acid
Essential amino acid
-
 NFC
NFC
-
 Synapse
Synapse
-
 Supergene
Supergene
-
 Anti-oncogene
Anti-oncogene
-
 Stream bed
Stream bed
-
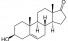 DHEA
DHEA
-
 E=mc²
E=mc²
-
 Crustacean
Crustacean
-
 Drag
Drag
-
 Neanderthal
Neanderthal
-
 Haplotype
Haplotype
-
 Isomerase
Isomerase
Ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetic materials have the property of becoming magnetic, i.e. of being magnetised, when placed in a magnetic field, and of keeping part of this magnetism when the field is removed.
Ferromagnetic materials are composed of metal elements such as iron (mainly), nickel and cobalt that allow strong magnetisation to be achieved.
The interior of ferromagnetic materials is split into small domains in which all the atoms have parallel magnetisation. These domains tend to align in the direction of an external magnetic field, making the material strongly magnetic.
Ferromagnetic substances are used for their magnetic properties because, not only can they be strongly magnetised, they can remain so through the magnetic hysteresis phenomenon.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



