-
 Antimetabolite
Antimetabolite
-
 Lintel
Lintel
-
 Basal shoot
Basal shoot
-
 Algorithmics
Algorithmics
-
 Active galaxy nucleus
Active galaxy nucleus
-
 Turbidity
Turbidity
-
 Abortion
Abortion
-
 Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis
-
 Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E
-
 Genomic
Genomic
-
 Granulocyte
Granulocyte
-
 Cuculiformes
Cuculiformes
-
 Partial unbundling
Partial unbundling
-
 Kuiper belt
Kuiper belt
-
 Powdery
Powdery
-
 Caruncle
Caruncle
-
 Kilobar
Kilobar
-
 Artemisin
Artemisin
-
 Arend-Roland comet
Arend-Roland comet
-
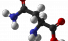 Asparagine
Asparagine
-
 Residual error rate
Residual error rate
-
 M92
M92
-
 Radiosensitive
Radiosensitive
-
 Exfoliation
Exfoliation
-
 Hybrid vehicle
Hybrid vehicle
-
 SMS
SMS
-
 TSI
TSI
-
 VOC
VOC
-
 Volcano
Volcano
-
 Osteoclast
Osteoclast
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by the protozoon Toxoplasma gondii. It mostly infects warm-blooded animals including human beings. Cat species are the obligate hosts . The disease is mild or even asymptomatic in the great majority of cases. A third of the population worldwide is even thought to be infected. However, it is dangerous to the seronegative pregnant woman (a person who does not have antibodies against toxoplasmosis in their blood) as she may transmit the Toxoplasma to her foetus. The resultant toxoplasmosis can even sometimes kill the foetus.
Transmission of toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is transmitted by cats. The Toxoplasma colonises the cat's small intestine and is excreted in their faeces. The disease only develops if these parasites are ingested. The risk is therefore low and occurs at the time when the cat litter is changed .
Toxoplasmosis in adults
Toxoplasmosis is asymptomatic in the very great majority of cases. Only immunosuppressed people (such as AIDS suffers) are at risk of the effect of a parasite. They can then develop lesions in their eyes, cardiac, respiratory and even nervous systems combined with a fever.
Toxoplasmosis during pregnancy
Toxoplasmosis is transmitted from the mother to the child across the placenta, only if the mother is seronegative (if she does not have antibodies against the parasite). The risk of transmission increases during the pregnancy and reaches a peak after 36 weeks of gestation. On the other hand, the later the foetus is infected the less severe the infection is. During pregnancy:
- the infection occurs during the first trimester of pregnancy, it may result in the foetus dying either at that time or in the first months of life after birth. The babies that survive can suffer many neurological problems, particularly psychomotor retardation;
- if the infection occurs during the second trimester, central nervous system problems are less likely;
- if infection occurs during the third trimester of pregnancy the risks are only ophthalmological with pigmented chorioretinitis (abnormal pigmentation in the retina). In 80% of cases the baby has no signs at birth although symptoms may develop throughout childhood and even in adolescence. Long term monitoring is therefore needed.
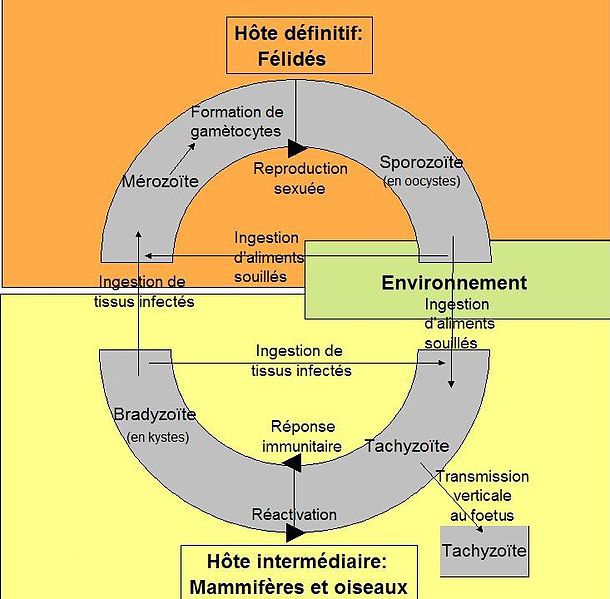 During the life cycle of the toxoplasmosis vector in passes through several phases and changes host before obligate infection of a cat species. © Powch, Wikipedia, cc by sa 3.0
During the life cycle of the toxoplasmosis vector in passes through several phases and changes host before obligate infection of a cat species. © Powch, Wikipedia, cc by sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



