-
 Trophallaxis
Trophallaxis
-
 Vortex
Vortex
-
 Riparian
Riparian
-
 Epitaxy
Epitaxy
-
 Pre-combustion separation of CO2
Pre-combustion separation of CO2
-
 Bayer name
Bayer name
-
 Amnesia
Amnesia
-
 Stimulation
Stimulation
-
 Epithelium
Epithelium
-
 Sensitive Natural Space
Sensitive Natural Space
-
 Sale by the cord
Sale by the cord
-
 Pomegranate
Pomegranate
-
 Opposition
Opposition
-
 Javascript
Javascript
-
 M8
M8
-
 Filiform
Filiform
-
 Deciduous forest
Deciduous forest
-
 Pathogenicity
Pathogenicity
-
 Orthosilicate
Orthosilicate
-
 Fanconi anaemia
Fanconi anaemia
-
 Copenhagen interpretation
Copenhagen interpretation
-
 Decarbonation
Decarbonation
-
 Focal epilepsy
Focal epilepsy
-
 Rosetta
Rosetta
-
 DOUBLE STAR
DOUBLE STAR
-
 Expectoration
Expectoration
-
 Telnet
Telnet
-
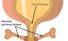 Urethra
Urethra
-
 LAN
LAN
-
 Cuneiform
Cuneiform
Sialography
Sialography is the radiological examination which investigates the salivary, submandibular or parotid glands (beneath the ear). The examination is performed by a radiologist either in a private centre or in a hospital.
Sialography the process
Sialography examines the different salivary glands and is used particularly to assess salivary stones. It can be used to investigate for stones, to determine how many there are and precisely where they are. Possible malformations or narrowing of the excretory ducts can also be revealed.
The examination procedure
The patient sits on the examination table where the radiologist takes films before the injection. Secondarily, he/she places a small catheter into the entrance to the salivary gland duct. And may ask the patient to drink a few drops of lemon juice to increase saliva production and facilitate the examination. The radiologist then injects the contrast medium which makes the duct and gland visible to X-rays. Films are then taken in different positions to study the contours of the gland. Whilst these are being taken the patient must not move. The examination is quick. It lasts around twenty minutes.
The possible risks of sialography
Complications are extremely rare. The contrast medium may potentially cause allergic reaction.
Sources:
- Cornouaille Hospital, Quimper;
- Rennes Faculty of Medicine, accessed on 18 February 2011.
 “AAA” Sialography. © Phovoir
“AAA” Sialography. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



