-
 Permanent virtual circuit
Permanent virtual circuit
-
 Emission spectrometry
Emission spectrometry
-
 Electronegativity
Electronegativity
-
 Allosteric site
Allosteric site
-
 Forums
Forums
-
 Herpes
Herpes
-
 Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis
-
 Chitin
Chitin
-
 International Astronomical Union
International Astronomical Union
-
 Dashboard
Dashboard
-
 Typhoid fever
Typhoid fever
-
 Anion
Anion
-
 ERS-2
ERS-2
-
 Heritage species
Heritage species
-
 Parallax barrier
Parallax barrier
-
 Axial
Axial
-
 Scar
Scar
-
 Residue
Residue
-
 Asthenosphere
Asthenosphere
-
 Broad Bean
Broad Bean
-
 Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
-
 FEAL
FEAL
-
 Chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy.
-
 Thoracic cavity
Thoracic cavity
-
 Google Desktop
Google Desktop
-
 Glycopeptide
Glycopeptide
-
 MP3
MP3
-
 Optical doublet
Optical doublet
-
 Coelacanth
Coelacanth
-
 Propellant
Propellant
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an acute respiratory infection affecting the lungs. The lung alveoli, which are responsible for gas exchange fill with fluid, making respiration difficult. 1.8 million children around the world die from pneumonia each year making it the leading cause of infant mortality.
Pneumonia agents
Pneumonia can be caused by various pathogens (bacteria, viruses, and fungi). The most common include the Pneumococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae), bacteria Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), the Respiratory Syncytial Virus, and the fungus Pneumocystis jirovec.
Transmission of pneumonia
The pathogens infect the respiratory tract and are transmitted by droplet inhalation produced by an infected person sneezing or coughing. They are also believed to be transmissible through the blood. The weakest people particularly the immunosuppressed (people with HIV or measles) are more sensitive to the disease. Passive smoking in children is also a risk factor for pneumonia.
Symptoms of pneumonia
Depending on the pathogen involved, symptoms may be more ore less severe. Fast or difficult respiration, cough, temperature, shivering, anorexia, or wheezing are usually seen however.
Treatment of pneumonia
Whereas bacterial pneumonias are treated with antibiotics, viral or fungal pneumonias are more difficult to treat. The youngest children are cared for in hospital.
Vaccines are available against the Pneumococcus and Hib. Vaccination against measles and whooping cough is also an effective means of prevention.
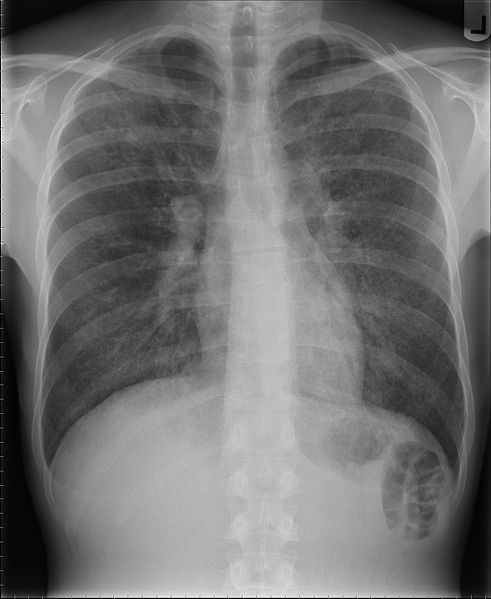 Pneumonia may be caused by Pneumocystis jiroveciinfection which is seen here on a lung radiograph. © Samir, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Pneumonia may be caused by Pneumocystis jiroveciinfection which is seen here on a lung radiograph. © Samir, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



