-
 Gastrin
Gastrin
-
 Agglutination
Agglutination
-
 Sea ice - Whitish
Sea ice - Whitish
-
 MOSS
MOSS
-
 Vortex
Vortex
-
 Concorde
Concorde
-
 Mountain pine
Mountain pine
-
 Microgranular rock
Microgranular rock
-
 Bandage
Bandage
-
 Digital signature
Digital signature
-
 DSP
DSP
-
 Occiput
Occiput
-
 Catalytic site
Catalytic site
-
 Catalpa
Catalpa
-
 Biofilter
Biofilter
-
 Switch
Switch
-
 Cystectomy
Cystectomy
-
 Dimorphous
Dimorphous
-
 ActiveX
ActiveX
-
 WYSIWYG
WYSIWYG
-
 Ecomobility
Ecomobility
-
 Strange quark
Strange quark
-
 Gastric
Gastric
-
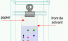 Chromatography
Chromatography
-
 Torrent
Torrent
-
 Abnormality
Abnormality
-
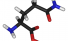 Glutamine
Glutamine
-
 End piece
End piece
-
 Winter squash
Winter squash
-
 Combustion
Combustion
Measles virus
The measles virus belongs to the Paramyxoviridae family and Morbilivirusgenus.
Characteristics of the measles virus
The measles virus is a negative polarity RNAvirus which has a linear genome of approximately 15,000 bases. It codes for only seven proteins, including a RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. The viral particle is spherical with a diameter of 150 nanometres and is enveloped by a cell membrane.
Measles virus and measles
The virus is highly infectious and is transmitted via droplets suspended in air. The virus then colonises immune cells in the pharynx and lungs. It attaches to the cells by specific receptors that recognise the virus surface proteins (haemagglutinin). After fusion between the viral and cell membranes, the RNA surrounded by a nucleocapsid is released into the cell cytoplasm. The viral RNA is then transcribed into messenger RNAs which are translated by the cellular ribosome into proteins required for the viral cycle. Finally the RNA is replicated to recreate new virions.
The new virions can then gradually colonise secondary lymphoid tissues, the skin and central nervous system.
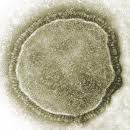
The measles virus is spherical and enveloped within a membrane. © AJC1, Flickr, CC by-nc-sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



