-
 Immunity
Immunity
-
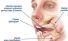 Salivary gland
Salivary gland
-
 Pike
Pike
-
 Germanium
Germanium
-
 Piscivore
Piscivore
-
 Mobility
Mobility
-
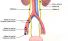 Ureter
Ureter
-
 Pubescent
Pubescent
-
 Arthropyosis
Arthropyosis
-
 Cath
Cath
-
 Polysynthetic
Polysynthetic
-
 PREBAT
PREBAT
-
 EFSA
EFSA
-
 Meteosat
Meteosat
-
 Local zoning plan
Local zoning plan
-
 Bok globules
Bok globules
-
 AIFF
AIFF
-
 Inhalation
Inhalation
-
 Adiabatic
Adiabatic
-
 Nucleosome
Nucleosome
-
 Anti-diarrhoeal agent
Anti-diarrhoeal agent
-
 Tholin
Tholin
-
 Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance
-
 Cerebrovascular accident
Cerebrovascular accident
-
 Astrometric direction
Astrometric direction
-
 Stellarator
Stellarator
-
 Nuptial plumage
Nuptial plumage
-
 CNG
CNG
-
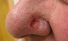 Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma
-
 FIPS
FIPS
MAO-B inhibitor
The monoamine oxidase B inhibitors (MAO-B) are medicines used to treat Parkinson's disease. They are administered orally often in combination with L-dopa (Levodopa).
How do the MAO-B inhibitors work?
The MAO-B inhibitors reduce the degradation of dopamine which is produced as a result of another antiparkinsonian treatment, levodopa. MAO-B is an enzyme which naturally degrades dopamine in the brain. This then prolongs the action of L-dopa.
Do they have contraindications or precautions?
MAO-B inhibitors are associated with a relatively large number of side effects. These include headaches (when administered alone as monotherapy) dyskinesia, vomiting, constipation and bodily accidents. When they are administered with L-dopa, a drop in blood pressure may also occur when the person is standing. Thos is also known as orthostatic hypotension.
Sources:
- Merck Manual, 4th edition
- Interview with Jean-Philippe Brandel, neurologist at the Léopold Bellan Hospital, Paris on www.infopatients-lundbeck.fr, 7 July 2011
- MyPDinfo.com, 7 July 2011
 MAO-B inhibitors reduce the degradation of dopamine. © Phovoir
MAO-B inhibitors reduce the degradation of dopamine. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



