-
 Arctic fulmar
Arctic fulmar
-
 Work hardening
Work hardening
-
 Tiagabine
Tiagabine
-
 Vertebral column
Vertebral column
-
 Dry ice
Dry ice
-
 Principle of action and reaction
Principle of action and reaction
-
 Small Magellanic cloud
Small Magellanic cloud
-
 Wolframite
Wolframite
-
 Black smoke
Black smoke
-
 Solvay congress
Solvay congress
-
 Elementary particle physics
Elementary particle physics
-
 Colony
Colony
-
 Pneumatophore
Pneumatophore
-
 Lipid
Lipid
-
 Metamict
Metamict
-
 Basiphilous
Basiphilous
-
 High energy performance
High energy performance
-
 Carnot cycle
Carnot cycle
-
 Colour rendering index
Colour rendering index
-
 Weak opiate analgesic
Weak opiate analgesic
-
 Salt gland
Salt gland
-
 Progestogen
Progestogen
-
 URL
URL
-
 Solfatare
Solfatare
-
 Wading bird
Wading bird
-
 USB
USB
-
 Algal film
Algal film
-
 Neovascularisation
Neovascularisation
-
 Cross linking
Cross linking
-
 Salivary gland
Salivary gland
Lysosome
A lysosome is a eukaryotic cell organelle.
Structure of the lysosome
The lysosome is a small spherical structure (a vesicle) delineated by a lipid membrane and located in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. The membrane contains ion channels (proton pumps) which allows active intake of H+ ions in order to maintain an acid pH (between 3.5 and 5) within the lysosomal vesicle.
Role of the lysosome
The lysosome acts as a cell dustbin where non-functional molecules are removed by digestion. The lysosome contains hydrolases, enzymes intended to degrade intracellular molecules. They are only active in an acid pH, hence the low pH in the vesicle.
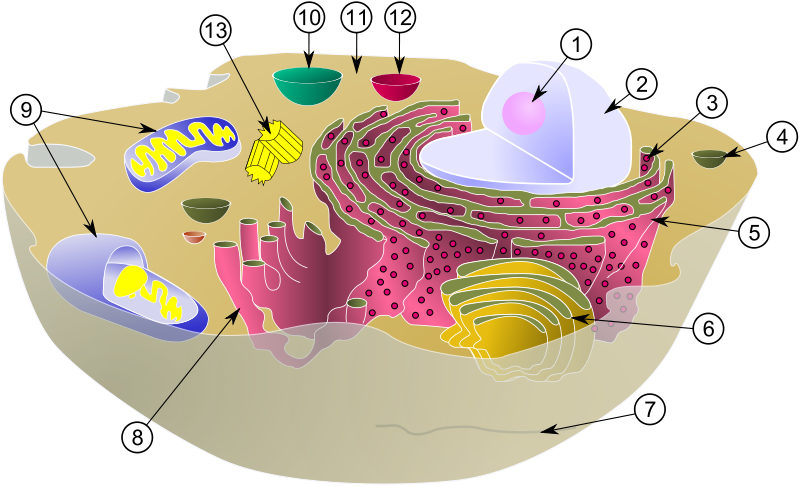 Diagram of a typical animal cell with its organelles: 1. Nucleolus; 2. Nucleus; 3. Ribosome; 4. Vesicle; 5. Rough (or granular) endoplasmic reticulum also called the ergastoplasm; 6. Golgi apparatus; 7. Cytoskeleton ; 8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum ; 9. Mitochondrium ; 10. Vacuole ; 11. Cytosol ; 12. Lysosome ; 13. Centriole. © MesserWoland et Szczepan1990, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Diagram of a typical animal cell with its organelles: 1. Nucleolus; 2. Nucleus; 3. Ribosome; 4. Vesicle; 5. Rough (or granular) endoplasmic reticulum also called the ergastoplasm; 6. Golgi apparatus; 7. Cytoskeleton ; 8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum ; 9. Mitochondrium ; 10. Vacuole ; 11. Cytosol ; 12. Lysosome ; 13. Centriole. © MesserWoland et Szczepan1990, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



