-
 Fosfomycin
Fosfomycin
-
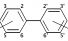 PCB
PCB
-
 Norite
Norite
-
 Entomology
Entomology
-
 Sex glands
Sex glands
-
 Chiropraxis
Chiropraxis
-
 Dry ice
Dry ice
-
 Radiometer
Radiometer
-
 Lacunar circulation
Lacunar circulation
-
 Fermentation
Fermentation
-
 Gram positive bacterium
Gram positive bacterium
-
 Bandage
Bandage
-
 Telepoint
Telepoint
-
 Fairing
Fairing
-
 New Technology Telescope
New Technology Telescope
-
 Calyx
Calyx
-
 Nymphosis
Nymphosis
-
 Infuse
Infuse
-
 H.262
H.262
-
 Narcotic
Narcotic
-
 Soot
Soot
-
 Agglutinin
Agglutinin
-
 Galileo
Galileo
-
 Growth twin
Growth twin
-
 Adduction
Adduction
-
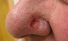 Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma
-
 Depleted uranium
Depleted uranium
-
 Prompt
Prompt
-
 Oscillograph
Oscillograph
-
 Single-stranded
Single-stranded
Lipid
Lipids are fats, i.e. hydrophobic or amphipathic molecules (one hydrophobic part and one hydrophilic part).
Features of lipids
Lipids are characterised by the fact that they are insoluble in water and, conversely, are soluble in non-polar organic solvents.
Diversity of lipids
There are eight varieties of lipids according to the UPAC classification:
- fatty acids (including omega-3);
- acylglycerols (or glycerides, including triglycerides) ;
- phosphoacylglycerols (or phosphoglycerides;
- sphingolipids ;
- sterols (including cholesterol) ;
- prenols;
- polyketides ;
- saccharolipids (or glycolipids).
Role of lipids
Waxes and vegetable oils are formed from lipids. Lipids in the diet provide the largest number of calories (9.3 kilocalories per gram).
Lipids carry out a wide range of biological functions including:
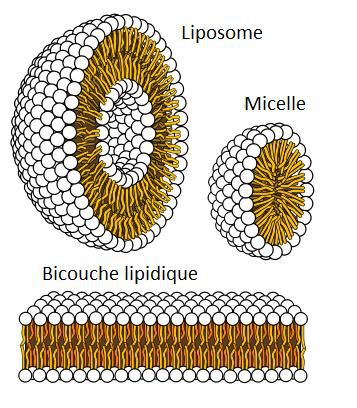 The amphiphatic side of lipids pushes them to bind to each other so they avoid contact with water. The hydrophilic parts (in white) remain in contact with water, whereas the hydrophobic parts (in yellow) remain bound. This effect leads to the formation of liposomes, micelles, or the lipid bilayer (of cell membranes). © Public domain
The amphiphatic side of lipids pushes them to bind to each other so they avoid contact with water. The hydrophilic parts (in white) remain in contact with water, whereas the hydrophobic parts (in yellow) remain bound. This effect leads to the formation of liposomes, micelles, or the lipid bilayer (of cell membranes). © Public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



