-
 Google Earth
Google Earth
-
 Maculopapular rash
Maculopapular rash
-
 Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance
-
 Arp's loop
Arp's loop
-
 Astrocyte
Astrocyte
-
 Repudiation
Repudiation
-
 Redundant Code
Redundant Code
-
 Biosphere
Biosphere
-
 Blepharitis
Blepharitis
-
 Tephrite
Tephrite
-
 Essential nutrient
Essential nutrient
-
 Acrotonic
Acrotonic
-
 HCFC
HCFC
-
 Dehnel phenomenon
Dehnel phenomenon
-
 Ichneumonidae
Ichneumonidae
-
 Medical team
Medical team
-
 Winter squash
Winter squash
-
 Jatropha
Jatropha
-
 Phytohormone
Phytohormone
-
 Progestogen pill
Progestogen pill
-
 Biotic crisis
Biotic crisis
-
 Compressed air engine
Compressed air engine
-
 Pyroclastic flow
Pyroclastic flow
-
 EFSA
EFSA
-
 Pyroclastic surge
Pyroclastic surge
-
 Plinian spine
Plinian spine
-
 Weed
Weed
-
 Twinned crystal
Twinned crystal
-
 Atmosphere
Atmosphere
-
 To emulate
To emulate
Insulin
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone involved in the glucose cycle.
Structure of insulin
Insulin is composed of two peptide chains (A and B, 21 and 30 amino acids long respectively) connected to each other by two disulphide brides from cysteine groups.
Function of insulin
It is synthesised by the β islets of Langerhans cells in the pancreas insulin enables glucose to be taken up by muscle cells and adipocytes and converted into glycogen or fatty acids. It is therefore a hormone reducing blood sugar
Its role is to maintain constant blood glucose concentrations Diabetes, develops when insufficient insulin is secreted. This is why diabetic patients are given regular insulin injections
Resistance to insulin develops in elderly people. Their tissues no longer respond as well to insulin as they did previously. The consequences of this resistance firstly include an increase in insulin concentrations in the blood (which may appear paradoxical but is entirely logical) and secondly the development of metabolic disorders which predispose to accumulation of fat, which in turn contributes to deterioration of the arterial wall. Treatment of this type of dysfunction is one of the major research subjects into the effects of ageing and all the more so as it is currently only partly treated locally.
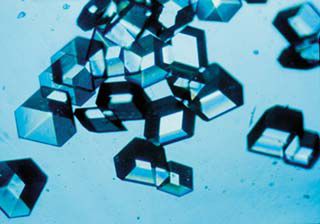
Insulin is a blood glucose lowering hormone. Here, it is in crystal form. © Nasa, Wikimedia, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



