-
 Choline
Choline
-
 Glinide
Glinide
-
 Protist
Protist
-
 Accretion disk
Accretion disk
-
 Drapery
Drapery
-
 Constellation of Leo
Constellation of Leo
-
 Shipwreck of the Ievoli Sun
Shipwreck of the Ievoli Sun
-
 Increment
Increment
-
 Télétel
Télétel
-
 FDD
FDD
-
 Winter solstice
Winter solstice
-
 Dinosaur
Dinosaur
-
 Hydrothermal circulation
Hydrothermal circulation
-
 Genesis 1
Genesis 1
-
 Lungfish
Lungfish
-
 Apex
Apex
-
 Cholestasis
Cholestasis
-
 Ohm
Ohm
-
 CD-TV
CD-TV
-
 Bearded seal
Bearded seal
-
 Dengue fever
Dengue fever
-
 Disseminated deposit
Disseminated deposit
-
 Mesosphere
Mesosphere
-
 Telnet
Telnet
-
 Ion exchanger
Ion exchanger
-
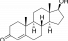 Testosterone
Testosterone
-
 Avifauna
Avifauna
-
 Object-oriented language
Object-oriented language
-
 Tidal bore
Tidal bore
-
 Postulate
Postulate
Hyperkalaemia
Hyperkalaemia is a pathological state in which excess potassium (Latin name: kalium) is present in blood plasma. In human beings this is defined as a concentration of over 5 mmol/L. A cardiac arrest may occur at any time at levels of 7 mmol/L and above, making hyperkalaemia a dangerous condition.
It is usually detected by chance as it has no specific symptoms. In reality everything depends on the concentration.
Causes of hyperkalaemia
Hyperkalaemia has many causes The most common include:
- renal failure ;
- some medicines;
- excess intravenous potassium;
- insulin deficiency (type 1 diabetes).
Treatments of hyperkalaemia
The aim of treatment above all is to avoid a cardiac arrest. Various treatments are used.
- Calcium gluconate: calcium has a potassium antagonising effect. This is short-acting, however, and the injection needs to be repeated regularly;
- An injection of insulin through an infusion of a glucose solution. Glucose needs potassium to enters cells. The potassium is then taken up by the cells rather than remaining in the blood circulation;
- Administration of betamimetics…
When hyperkalaemia is very serious and is immediately life-threatening, haemodialysis is used to cleanse the blood.
 A blood sample is needed to measure the potassium concentration in blood. Hyperkalaemia exists if the concentration is over 5 mmol/L. © Newbitrh35, Flickr, cc by nc 2.0
A blood sample is needed to measure the potassium concentration in blood. Hyperkalaemia exists if the concentration is over 5 mmol/L. © Newbitrh35, Flickr, cc by nc 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



