-
 Nucleus
Nucleus
-
 Critical temperature
Critical temperature
-
 Inclination
Inclination
-
 Complication
Complication
-
 Differential interference contrast microscope
Differential interference contrast microscope
-
 Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine
-
 Mean equatorial of the date
Mean equatorial of the date
-
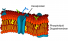 Plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
-
 Saturated fatty acid
Saturated fatty acid
-
 Obliquity
Obliquity
-
 Reproductive success
Reproductive success
-
 Vigabatrin
Vigabatrin
-
 MA
MA
-
 Dry process
Dry process
-
 Disseminated
Disseminated
-
 Alluvial deposit
Alluvial deposit
-
 Recrystallisation
Recrystallisation
-
 Pipeline
Pipeline
-
 H.261
H.261
-
 End piece
End piece
-
 Breadfruit
Breadfruit
-
 Bird songs
Bird songs
-
 Quinolone
Quinolone
-
 Bonding
Bonding
-
 A rare disease
A rare disease
-
 YUV
YUV
-
 CCSM
CCSM
-
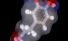 Dopamine
Dopamine
-
 Eisenmenger complex
Eisenmenger complex
-
 Cillosis
Cillosis
Fibrillar bone
Because of the spatial organisation of the extracellular bone matrix (EBM), fibrillar bone is distinguished from lamellar bone. The collagen bundles in fibrillar bone are arranged in all directions whereas lamellar bone has a regular structure.
Wherever bone tissue has to be formed very quickly, fibrillar (or primary or immature bone, during development or recovery from a fracture), whereas lamellar (or mature) bone occurs secondarily and requires more time to form. Lamellar bone is formed from spongiform (or canalicular) bone (Spongiosa) and compact bone (Kompakta), which are both lamellar in structure. They are only different in the way in which their fibres are organised. Canalicular bone is made up of flat fibres parallel to its surface whereas a compact bone is made up of concentric fibres arranged around a blood vessel. The lamellar structure can be seen under a polarising microscope.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



