-
 ATM
ATM
-
 Free radical
Free radical
-
 Lyme's Disease
Lyme's Disease
-
 Megacycle
Megacycle
-
 Unbounded universe
Unbounded universe
-
 Arctic
Arctic
-
 Zebrafish
Zebrafish
-
 MicroRNA
MicroRNA
-
 Sedimentary basin
Sedimentary basin
-
 Charter for the Environment
Charter for the Environment
-
 Quark
Quark
-
 Perovskite
Perovskite
-
 Brightening
Brightening
-
 Epiphysis
Epiphysis
-
 Air
Air
-
 Amblyopia
Amblyopia
-
 Crystal class
Crystal class
-
 Heliopause
Heliopause
-
 Anode
Anode
-
 Lacunar circulation
Lacunar circulation
-
 Amyotrophy
Amyotrophy
-
 Induction
Induction
-
 Western hemlock
Western hemlock
-
 Oviparous
Oviparous
-
 Alar bar
Alar bar
-
 Eclipse of the Moon
Eclipse of the Moon
-
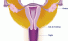 Vagina
Vagina
-
 Robot
Robot
-
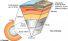 Mantle
Mantle
-
 Electrochemical cell
Electrochemical cell
Echocardiography
Echocardiography is ultrasound... of the heart. The technique uses ultrasound. The principle involves recording the electrical potentials which control cardiac activity using an instrument which amplifies the signals. These are then re-transcribed and analysed. The examination is performed by a cardiologist either in a hospital or in specialist consulting rooms.
Echocardiography, the process
Echocardiography reproduces an image of the heart and the great vessels. It is therefore used to examine cardiac dynamics and the thickness of the walls of the heart. It also provides information about the presence of any areas of ischaemia in infarction. It can be used to demonstrate a malformation or a tumour. TM mode (Time Motion) enables echocardiography to study the movements of the cardiac walls and valves. On the other hand, two-dimensional echocardiography studies the morphology and kinetics of the heart valves and the various features of the heart as it functions.
The examination process
The patient is naked to the waist and lies on his/her back. The cardiologist may ask the patient to turn onto his/her left side in order to improve image quality. The cardiologist will then apply a gel to the skin which promotes transmission of the ultrasound. The investigation lasts 10 to 30 minutes during which the cardiologist records images and takes measurements.
Possible risks of echocardiography
These are the same as for any other ultrasound. In other words it carries no risks. Ultrasound has no side effects or contraindications. It does not use X-rays and therefore is not irradiating.
Source : Merck Manual, 4th edition
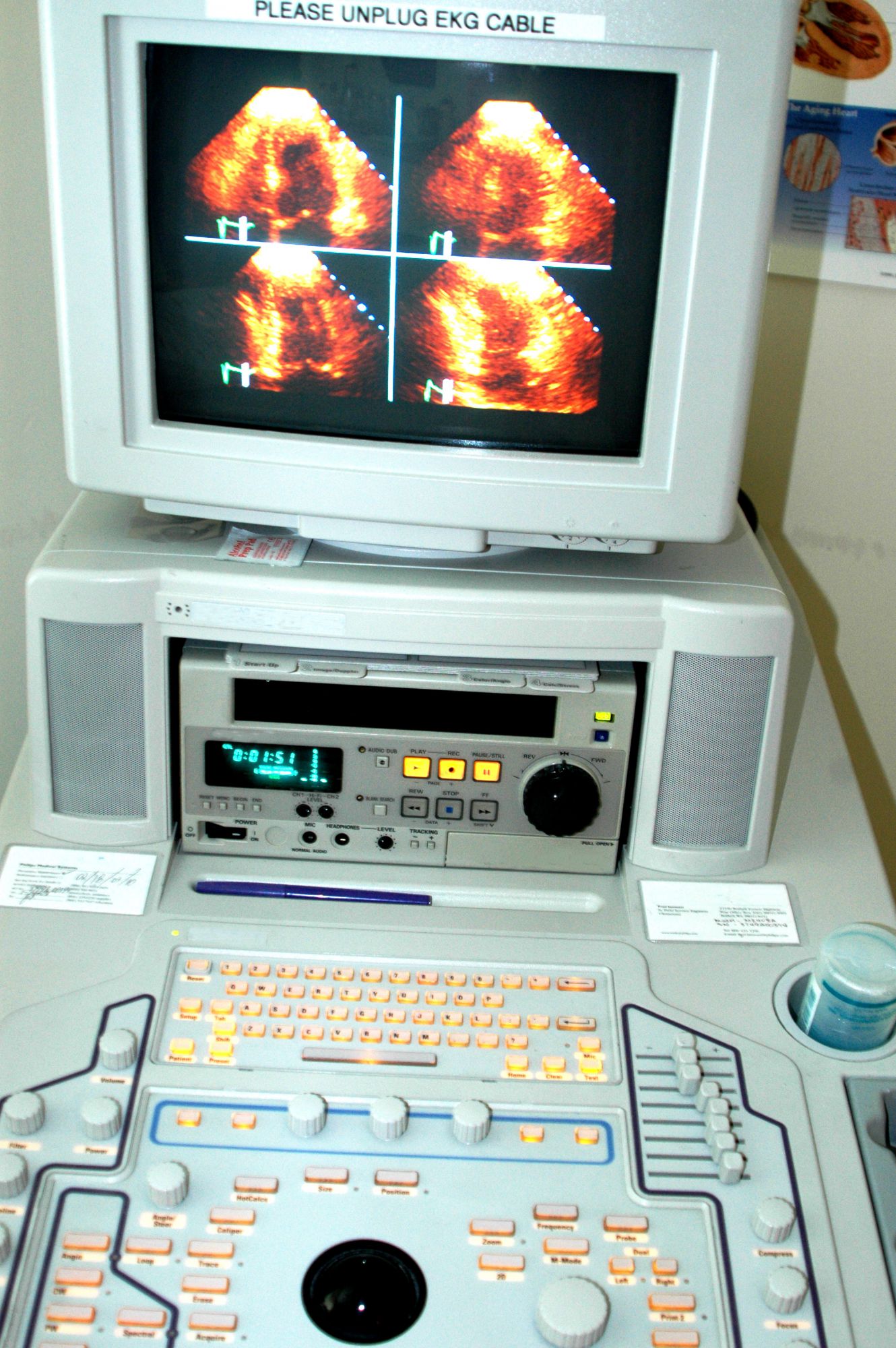 Echocardiography: an ultrasound of the heart. © Robert Lerich
Echocardiography: an ultrasound of the heart. © Robert Lerich
Latest
Fill out my online form.



