-
 Over-packaging
Over-packaging
-
 Asteroid belt
Asteroid belt
-
 Homeotic gene
Homeotic gene
-
 Colour
Colour
-
 Planking
Planking
-
 Nova
Nova
-
 Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
-
 Aulacogen
Aulacogen
-
 Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy
-
 ISP
ISP
-
 Dysgraphia
Dysgraphia
-
 Survival function
Survival function
-
 Mars Sample Return
Mars Sample Return
-
 Cubic system
Cubic system
-
 DVB-SH
DVB-SH
-
 SGML
SGML
-
 Windscale nuclear power station fire
Windscale nuclear power station fire
-
 Ephemeris meridian
Ephemeris meridian
-
 Solenoid
Solenoid
-
 Adware
Adware
-
 Symbian
Symbian
-
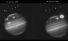 Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet
Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet
-
 Interference
Interference
-
 Nuisance
Nuisance
-
 Dreikanter
Dreikanter
-
 Hexagonal system
Hexagonal system
-
 Ogino method
Ogino method
-
 Liquid Audio
Liquid Audio
-
 Pixel
Pixel
-
 Typhoid fever
Typhoid fever
Combined pill
Combined pills are also described as estrogen-progestogen pills and contain two synthetic hormones: a estrogen and a progestogen. These oral contraceptives usually need to be taken daily at the same time for 21 or 24 days.
How do combined pills work?
Combined pills mostly act by blocking ovulation. The hormones that they contain act on the hypothalamus, which controls the production of sex hormones. They stimulate the action of natural hormones, blocking the release of gonadotrophins which stimulate ovulation. The endometrium becomes thinner and the cervical mucus thickens making nidation of the fertilised egg in the uterus impossible.
Contraindications or precautions?
Combined pills can cause metrorrhagia. This means uterine bleeding between menstrual periods. Estrogens can also cause salt and water retention which in turn can be linked to a reversible rise in blood pressure and even weight gain. The weight gain may be as much as 2 kilograms. The progestogens can cause androgenic effects which can cause acne, anxiety or weight gain. The risk of deep vein thrombosis and thrombo-embolic accidents also increases in parallel with the dose of estrogens. The relative risk - which it should be pointed out is still low - is therefore greater in women who are taking pills containing a high dose of estrogens (more than 50 µg).
Conversely, there are contraindications to the use of some oral contraceptives: past history of thrombo-embolic disease, cerebrovascular or coronary artery disease, known or suspected breast cancer, past history of abnormal vaginal bleeding without a specific diagnosis. And of course, known or suspected pregnancy. Smoking and age increase the risk of cerebral vascular accident (CVA) and the incidence of death from complications of deep vein thrombosis.
Sources :
- Manuel Merck, 4th edition;
- Principles of Internal Medicine, T.R. Harrisson, Publisher Flammarion
 Combined pills contain an estrogen and a progestogen. © Phovoir
Combined pills contain an estrogen and a progestogen. © Phovoir
Latest
Fill out my online form.



