-
 Sequella
Sequella
-
 Dolomitic limestone
Dolomitic limestone
-
 Anticholinergic
Anticholinergic
-
 Peroxisome
Peroxisome
-
 Arthropyosis
Arthropyosis
-
 Parabens
Parabens
-
 ESTEC
ESTEC
-
 Horsepower
Horsepower
-
 InnoDB
InnoDB
-
 Alopecia
Alopecia
-
 Essential nutrient
Essential nutrient
-
 Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect
Sunyaev-Zel'dovich effect
-
 EADS
EADS
-
 Homo heidelbergensis
Homo heidelbergensis
-
 Floating screed
Floating screed
-
 Phases of the Moon
Phases of the Moon
-
 Public key
Public key
-
 Galvanic corrosion
Galvanic corrosion
-
 Moisture regime
Moisture regime
-
 Leukopenia
Leukopenia
-
 Wettability
Wettability
-
 Anti-g suit
Anti-g suit
-
 Weightlessness
Weightlessness
-
 Lithification
Lithification
-
 Codec
Codec
-
 Arms
Arms
-
 Curettage
Curettage
-
 Pathology
Pathology
-
 Aponeurosis
Aponeurosis
-
 Carbon credit
Carbon credit
Chikungunya virus
The Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is the agent responsible for Chikungunya disease.
Characteristics of the Chikungunya virus
The Chikungunya virus belongs to the Togaviridaefamily and Alphavirusgenus. It is a spherical viral particle with a diameter of 65 nanometres, which is enveloped and contains a single positive polarity RNA which codes for two polyproteins. The RNA is directly infectious and acts therefore both as the genome and as the messenger RNA. The 11 to 12,000 bases in its genome ultimately allow nine proteins to be synthesised which are obtained after cleavage of the polyproteins by viral and cell proteases.
At the end of the viral cycle which includes synthesis of the proteins, replication and assembly of the viral particles, the particles bud from the plasma membrane of the infected cells. The viral proteins are inserted into the membrane.
CHIKV and Chikungunya
The virus is transmitted to human beings from injection of anticoagulating saliva into the blood of the person bitten by a mosquito vector. It is now known that the virus does not infect circulating blood cells but rather macrophages and adherent cells (endothelial, epithelial, fibroblasts).
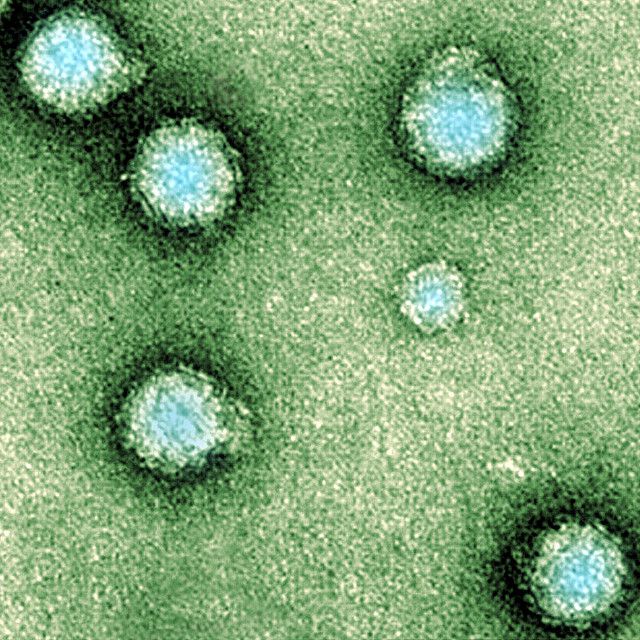 The Chikungunya virus is spherical in shape. © AJC1, Flickr, CC by-nc 2.0
The Chikungunya virus is spherical in shape. © AJC1, Flickr, CC by-nc 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



