-
 Cookie
Cookie
-
 Bartholin glands
Bartholin glands
-
 Time
Time
-
 NexGuard
NexGuard
-
 Chlorosity
Chlorosity
-
 Tectosilicates
Tectosilicates
-
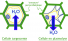 Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis
-
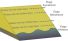 Foreshore
Foreshore
-
 Villi
Villi
-
 Gamete
Gamete
-
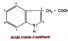 Auxin
Auxin
-
 Coelacanth
Coelacanth
-
 Lysosome
Lysosome
-
 Nanofluidics
Nanofluidics
-
 Grained rock
Grained rock
-
 Reflection microscope
Reflection microscope
-
 Lawson's cypress
Lawson's cypress
-
 Homolysis
Homolysis
-
 Liver fluke
Liver fluke
-
 Nintendo DS
Nintendo DS
-
 Dehydration
Dehydration
-
 Telematics
Telematics
-
 Pegasus
Pegasus
-
 Retreading
Retreading
-
 Apical apparatus
Apical apparatus
-
 Breast milk
Breast milk
-
 Limestone pavement
Limestone pavement
-
 Saturated fatty acid
Saturated fatty acid
-
 BCD galaxy
BCD galaxy
-
 Epicanthus
Epicanthus
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a predominantly cortical neurodegenerative dementia that primarily affects cognitive functions and has consequences on patients' behaviour and social adaptation.
On average, it occurs around the age of 65 years old and currently affects approximately 350,000 people in France. Because of its prevalence (5% of those over 65 years old, 20% of those over 80 years old) and its economic and social burden on society (70% of long-stay hospital beds) it is a major public health problem in all industrialised countries.
Different treatment approaches are being investigated, although the most promising appears to be the amyloid cascade.
One of the key questions for the pharmacology of Alzheimer's disease is the assessment of treatments: measurement criteria, significant of response, design of clinical trials, impact of concomitant medicines etc. Answers are beginning to be found to these questions and are part of an amazing scientific, medical and social adventure that has only just begun.
Latest
Fill out my online form.



