-
 Black walnut
Black walnut
-
 Oocyte
Oocyte
-
 Circuit routing
Circuit routing
-
 Cytostatic
Cytostatic
-
 Vaccine
Vaccine
-
 Aqua
Aqua
-
 Z-Machine
Z-Machine
-
 Epicentre
Epicentre
-
 Hash function
Hash function
-
 Widmannstätten
Widmannstätten
-
 HELIOS II
HELIOS II
-
 Taikonaut
Taikonaut
-
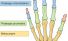 Metacarpus
Metacarpus
-
 Stalagmite
Stalagmite
-
 Planetary nebula
Planetary nebula
-
 Hedged farmland
Hedged farmland
-
 Biomass
Biomass
-
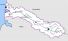 Drainage basin
Drainage basin
-
 Large Canary Island Telescope
Large Canary Island Telescope
-
 Ester bond
Ester bond
-
 Maltose
Maltose
-
 Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis
-
 Pollen
Pollen
-
 Gravitational lens
Gravitational lens
-
 Sign
Sign
-
 Kinase
Kinase
-
 Metamaterials
Metamaterials
-
 Skylab
Skylab
-
 ERS-2
ERS-2
-
 Antihypertensive
Antihypertensive
WEP
Wired equivalent privacy, WEP, is a security protocol specified in IEEE 802.11 standard for protecting wireless network users from hacking. The aim of WEP is to provide the same degree of confidentiality as hard wired systems.
When WEP is activated on a wireless network, each 802.11 packet is encrypted in an RC4 coded stream generated by a 64 bit key. This key is made up of a 24 bit IV (initialisation vector) and a 40 bit WEP key. The encrypted key is generated by an XOR (exclusive OR gate) between the original packet and the RC4 data stream. The IV is chosen by the sender and can be modified from time to time so that the packets are not all encrypted with the same stream.
In 2004, WEP was superseded by WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), and the current implementation is WPA-2.

WEP
Latest
Fill out my online form.



