-
 Light
Light
-
 Nonlinear crystal
Nonlinear crystal
-
 Authorisation certificate
Authorisation certificate
-
 Cauliflower
Cauliflower
-
 Swift
Swift
-
 Geosynchronous orbit
Geosynchronous orbit
-
 Scots pine
Scots pine
-
 DVI
DVI
-
 Higgs boson
Higgs boson
-
 Roziere balloon
Roziere balloon
-
 Colostrum
Colostrum
-
 Coupled reactions
Coupled reactions
-
 Endergonic
Endergonic
-
 Plinian spine
Plinian spine
-
 Aplysia
Aplysia
-
 Nectar
Nectar
-
 DSL
DSL
-
 Droppings
Droppings
-
 Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis
-
 LDAP
LDAP
-
 Precambrian
Precambrian
-
 Chalazion
Chalazion
-
 Twilight
Twilight
-
 M32
M32
-
 Vesta
Vesta
-
 Titan
Titan
-
 Cranberry
Cranberry
-
 HTML
HTML
-
 Pycnocline
Pycnocline
-
 Computer virus
Computer virus
Endoreduplication
Endoreduplication is the process by which a cell duplicates its genetic material but does not divide.
During mitosis, chromosomes are firstly separated and then each homologous chromosome migrates to a pole in the cell. Finally, the cell separates and the chromosomes are duplicated within the daughter cells. In endoreduplication, however, cell division does not take place although the genetic material which is duplicated is contained within the same cell, which then becomes polyploid.
Causes of endoreduplication
The factors which lead to endoreduplication are still relatively poorly understood although this phenomenon if often linked to high metabolic activity, for example grass after mowing, or in fruit formation (the different sizes of tomatoes for example represent different levels of endoreduplication).
Researchers assume that multiplication of genetic material leads to an increase in the expression of genes and therefore increased protein synthesis.
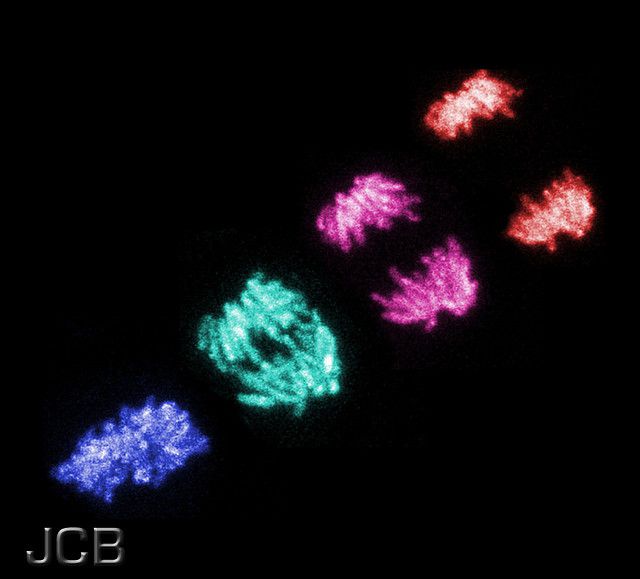 Endoreduplication is mitosis without cell division. © The JCB, Flickr, cc by nc sa 2.0
Endoreduplication is mitosis without cell division. © The JCB, Flickr, cc by nc sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



