-
 Chondrocyte
Chondrocyte
-
 Mantle
Mantle
-
 Elasticity
Elasticity
-
 Reducing agent
Reducing agent
-
 Acinar
Acinar
-
 Fossil fuel
Fossil fuel
-
 Depression
Depression
-
 Altruism
Altruism
-
 Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
-
 Blood group
Blood group
-
 Peas
Peas
-
 Colony
Colony
-
 Black hole
Black hole
-
 Radio telescope
Radio telescope
-
 Gill rakers
Gill rakers
-
 Up quark
Up quark
-
 Biome
Biome
-
 Ovulation
Ovulation
-
 Systemic antifungal
Systemic antifungal
-
 Diorite
Diorite
-
 PREBAT
PREBAT
-
 Door frame
Door frame
-
 Channelrhodopsin
Channelrhodopsin
-
 Diuretic
Diuretic
-
 Absolute zero
Absolute zero
-
 Transformation
Transformation
-
 Pentose
Pentose
-
 Pixel
Pixel
-
 Right ascension
Right ascension
-
 ADH
ADH
Adenosine
Adenosine is one of the building blocks of nucleic acids.
Structure of adenosine
Adenosine is produced by an adenine binding to a nitrogen base and a ribose (in RNA) or a deoxyribose (in DNA). Adenosine can be bound to phosphate groups. In this case we refer to adenosine monophosphate (AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), or adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Function of adenosine
Adenosine is involved in the formation of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). And it also plays major roles in metabolism.
In particular, ATP is an energy-containing molecule that releases energy by hydrolysing a phosphodiester bond.
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) is also a special molecule, as it acts as a switch in intracellular transmission.
Adenosine is also a hormonal neurotransmitter.
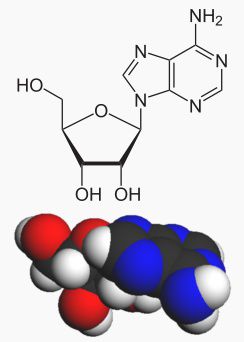
Adenosine is adenine bound to a ribose. © Wikimedia, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



