-
 Atrial flutter
Atrial flutter
-
 Flexography
Flexography
-
 Orphan disease
Orphan disease
-
 IFP
IFP
-
 CloudSat
CloudSat
-
 Polyp
Polyp
-
 Heisenberg equation
Heisenberg equation
-
 Hardness
Hardness
-
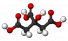 Citrate
Citrate
-
 Mublcom
Mublcom
-
 Osteoclast
Osteoclast
-
 Pelleting
Pelleting
-
 Exhaust velocity
Exhaust velocity
-
 Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy
-
 Internal energy
Internal energy
-
 Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis
-
 Cheilio
Cheilio
-
 Agroforestry
Agroforestry
-
 Fuel oxidizer
Fuel oxidizer
-
 Hypothesis
Hypothesis
-
 Cline
Cline
-
 Levorotatory
Levorotatory
-
 MVNO
MVNO
-
 Kipunji
Kipunji
-
 NexGuard
NexGuard
-
 Pathologist
Pathologist
-
 Infrared
Infrared
-
 Chicxulub
Chicxulub
-
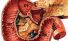 Duodenum
Duodenum
-
 Quantum entanglement
Quantum entanglement
Sclerenchyma
Sclerenchyma is a supporting tissue of vascular plants found in organs that have ceased lengthwise growth.
Description of sclerenchyma
In fact, the main characteristic of sclerous cells is that they are rigid and dead. Thus, they cannot grow longer. The walls of these cells are very thick and lignified. They therefore remain after the death of the cell and ensure the rigidity and impermeability of the plant.
Sclerenchyma consists of two types of cells:
- sclereids, which are short and of a variable shape, are isolated in the parenchyma or grouped together into foundation structures to consolidate certain organs;
- sclereid fibres, which are elongated and narrow, are found in a continuous ring or in fibre islands to support the plant.
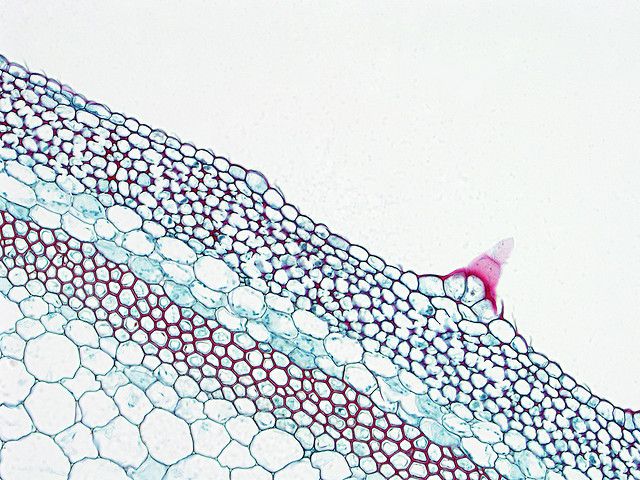 Cross section of a winter squash stem. The central cell layer consists of cells with thick, red couloured walls: this is the sclerenchyma. © BlueRidgeKitties CC by-nc-sa 2.0
Cross section of a winter squash stem. The central cell layer consists of cells with thick, red couloured walls: this is the sclerenchyma. © BlueRidgeKitties CC by-nc-sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



