-
 Granivore
Granivore
-
 Phoenicopteriformes
Phoenicopteriformes
-
 Stem cell
Stem cell
-
 Anxiolytic
Anxiolytic
-
 Satellite image
Satellite image
-
 Hexagonal system
Hexagonal system
-
 Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin
-
 Landsat
Landsat
-
 Centrifugal force
Centrifugal force
-
 Scalp
Scalp
-
 Syndrome
Syndrome
-
 Quiescence
Quiescence
-
 Steganography
Steganography
-
 Astroparticle
Astroparticle
-
 Ruptured aneurysm
Ruptured aneurysm
-
 Desertification
Desertification
-
 Substrate
Substrate
-
 Falconry
Falconry
-
 Nucleosome
Nucleosome
-
 Dynamic super-resolution microscope
Dynamic super-resolution microscope
-
 Adrenaline
Adrenaline
-
 Meningioma
Meningioma
-
 Active site
Active site
-
 Transalaska
Transalaska
-
 Droid
Droid
-
 Coverts
Coverts
-
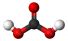 Carbonic acid
Carbonic acid
-
 Cellular dolomite
Cellular dolomite
-
 Mucilage
Mucilage
-
 Proterozoic era
Proterozoic era
Quinoa
There are over 2,000 varieties of quinoa. It is an herbaceous plant in the Chenopodiaceaefamily of which the seeds are harvested after maturation: it is not a cereal! The Native Altiplano Americans call this plant chisiya mama (in Quechua, "the mother of all grains") and consider it sacred as well as a symbol of the Earth's fertility.
After Spanish colonisation and the destruction of the traditional agricultural system, quinoa crops almost died out until recently when Bolivian and French researchers, amongst others, dedicated themselves to promoting it.

Bolivia: an experimental, standardised agricultural system comparing ten varieties of quinoa was created in 2003 in partnership with two university agriculture departments in the Molivian Altiplano, for research, training and development. The French Public Research Institute (IRD) and Bolivian partners dispensed participatory training days at different levels of university studies. Shown here are quinoa panicles.
© Raffaillac, Jean-Pierre/IRD - Base-indigo
The plant can grow to heights of up to 2 m and is grown on the Bolivian Altiplano at an altitude of 3,000 metres. For a long time quinoa was the daily staple of the Incas. Today it appears to be a possible solution to the world's hunger problem as it has exceptional nutritional value.
Properties of quinoa



Quinoa plays a primordial economic and dietary role in certain regions of Bolivia and elsewhere. Quinoa has major climatic constraints : especially frost and drought. In some areas the development of agricultural practices has led to ecosystem changes which are not always beneficial.

Quinoa panicles, milky toledo rojo seeds. On the Altiplano, a high plateau located at an altitude of between 3,600 and 4,300 metres, the research programme has developed an experimental agricultural network for quinoa, a pseudo-cereal which is generating growing interest as an organic, high protein content export to Europe and North America.
© Raffaillac, Jean-Pierre /IRD - Base-indigo
J.P.Raffaillac from the IRD, has researched this subject : "The work is on the identification of new plant cover conditions adapted to the physical limits of agro-ecosystems undergoing rapid change" (general objective of the UR CLIFA).
Work is focused on two themes
Functional solutions for quinoa growing in response to climatic constraints:
- anatomical and physiological adaptations to cold weather, drought and high radiation;
- relationships between plant cover architecture and plant temperature;
- variety and environmental effects: a network of agricultural experiments;
- genetic and environmental components of seed quality;
- water consumption by agriculture;
- modelling growing, cover and remote detection.
The role of agro-diversity in the sustainability of the crop system:
- Agro-diversity and climate variability;
- sustainability of the organic quinoa crop system in the Southern Altiplano.
Quinoa growing
Quinoa is grown as follows:
- fields are cultivated for one year and then left fallow for one year. Manure is spread before ploughing fields left fallow the previous year;
- manual sowing, or sowing using other traditional techniques,takes place in September in pockets of 100 to 150 seeds covered with wet soil;
- monitoring for caterpillar attacks during the growing season.
- Manual harvest in several passages depending on plant maturity;
- threshing and winnowing are done on site in the fields but must be finished before the May winds arrive due to the risk of contamination by sand which is nearly the same colour as the seeds. To be edible, quinoa must be rinsed of its bitter saponin film;
- and for export it must be washed, dried, sifted and packed in a cooperative factory. Its straw is used as fodder for llamas.

Quinoa seeds (highly enlarged: the actual diameter is 1 - 2 mm). © DR
Bibliography
- C. Aubert : L'assiette aux céréales
- C. Konig : course and personal notes (food)
Sitography
 Quinoa is a very nutritious food. © dana hilliot, Flickr CC by nc-sa 2.0
Quinoa is a very nutritious food. © dana hilliot, Flickr CC by nc-sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



