-
 Blandford-Znajek mechanism
Blandford-Znajek mechanism
-
 Gymnosperm
Gymnosperm
-
 Neoformation
Neoformation
-
 Paramagnetism
Paramagnetism
-
 Laboratory mouse
Laboratory mouse
-
 Echocardiography
Echocardiography
-
 Farad
Farad
-
 Flood plain
Flood plain
-
 Big Crunch
Big Crunch
-
 Metre
Metre
-
 Astrocytoma
Astrocytoma
-
 Polysynthetic
Polysynthetic
-
 FDA
FDA
-
 Total unbundling
Total unbundling
-
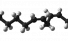 Linoleic acid
Linoleic acid
-
 Magma chamber
Magma chamber
-
 Torsion
Torsion
-
 Mean free path
Mean free path
-
 Detoxification
Detoxification
-
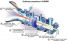 VASIMR
VASIMR
-
 Nuclear power plant
Nuclear power plant
-
 LISA
LISA
-
 Androgens
Androgens
-
 X-43
X-43
-
 Polygyny
Polygyny
-
 Carbon nanotube
Carbon nanotube
-
 PRAM
PRAM
-
 Unfractionated heparin
Unfractionated heparin
-
 Antisecretory H2 antagonist
Antisecretory H2 antagonist
-
 Stamping mill
Stamping mill
Downy oak
The downy oak is a beautiful tree which, in the South of France, sometimes reaches heights of 30 metres.
Names
The downy oak (Quercus pubescens), a member of the Fagaceae family, is also called the "pubescent oak".
Botanical description
The downy oak has a broad and clear crown. Its trunk is often short and twisted. Its blackish bark thickens with age and cracks quite quickly. The year's branches are pubescent and greyish. Its buds are brown, ovoid and pointed. Its deciduous leaves are alternate, smooth on top and pubescent underneath, with a limb 6 to 8 centimetres long and triangular, oblong lobes. This is a monoecious species which produces hanging, yellowish male catkins in April at the base of young branches. Its female flowers have bright red stigma and are located at the ends of the branches. Its sessile glands are clustered.

The trunk of the downy oak is often twisted. © remuz, Flickr CC 3.0 unported
Origins
The name of this species comes from the Latin word " pubescens ", which refers to the existence of short, soft hairs on the underside of the leaves and young branches, a method the tree uses to adapt to drought. This oak is especially found in Southern Europe and the Middle East. In France it is not found in the Brittany or Landes regions.

The downy oak has hair on the under side of its leaves. © dianesfra, Flickr CC 3.0 unported
Growing conditions
This species especially grows in rich, well-drained soil and tolerates calcareous soil.
Use
The wood of the downy oak is hard and difficult to work with and is therefore used mostly for heating. The major interest of this tree comes from it being a truffle tree, meaning that its presence encourages the growth of truffles.
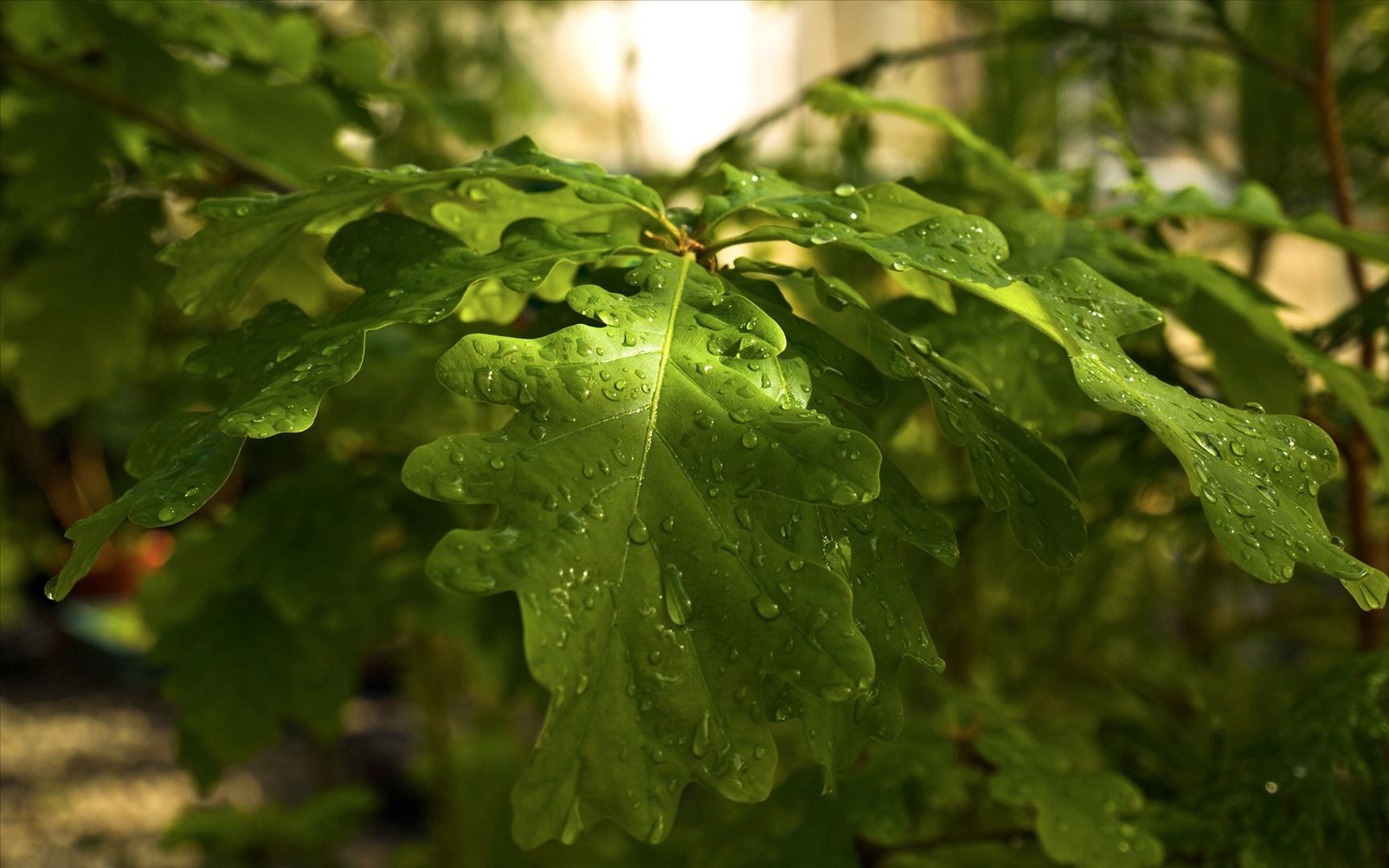 The downy oak. © axelkr, Flickr CC
The downy oak. © axelkr, Flickr CC
Latest
Fill out my online form.



