-
 Blogosphere
Blogosphere
-
 Van der Waals equation
Van der Waals equation
-
 Eutectic
Eutectic
-
 Modulation
Modulation
-
 MON810
MON810
-
 TCP/IP
TCP/IP
-
 Somite
Somite
-
 Ferrocene
Ferrocene
-
 Boxplot
Boxplot
-
 Thorax
Thorax
-
 Transplantation
Transplantation
-
 Inflorescence
Inflorescence
-
 Lava
Lava
-
 Radius
Radius
-
 CAPI
CAPI
-
 Isomerism
Isomerism
-
 Choroid
Choroid
-
 Substitution based encryption
Substitution based encryption
-
 Enzymatic
Enzymatic
-
 Highlighting
Highlighting
-
 Asymmetric keys
Asymmetric keys
-
 Gas planet
Gas planet
-
 Circuit breaker
Circuit breaker
-
 Stratification
Stratification
-
 Nucleon
Nucleon
-
 Access control
Access control
-
 Prime number
Prime number
-
 Bronchodilatator
Bronchodilatator
-
 Mechatronics
Mechatronics
-
 Fuselage
Fuselage
Collenchyma
Collenchyma is a supportive tissue of vascular plants that is mainly found in young organs and organs that grow upwards (stems, petiole, etc.).
The cells of this living tissue are characterised by very thick cellulose walls, a single, voluminous vacuole and a generally fusiform shape. This tissue gives a plant support and elasticity.
Different types of collenchyma
Depending on the thickness of this wall there are:
- annular collenchyma, with uniform cellulose deposits on the wall. This type of collenchyma rigidifies certain stems and petioles;
- angular collenchyma, where the thickening of the cellulose is concentrated in the corners of the wall;
- tangential collenchyma, where only the tangential walls, those parallel to the external surface, are thickened. This type of collenchyma is found in the bark of branches.
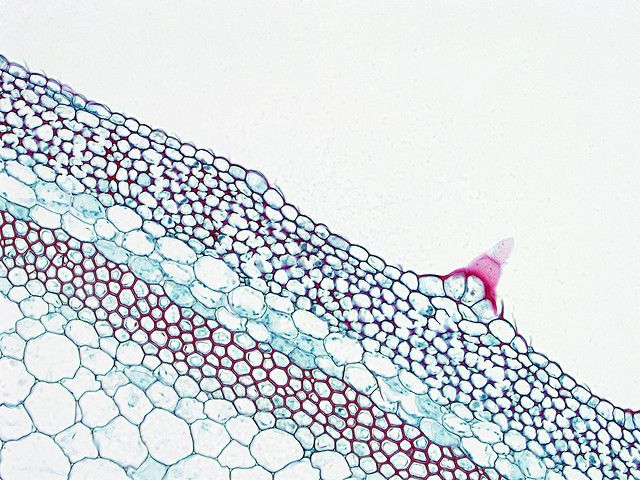 A cross section of a pumpkin stem. The cellular layer located under the epidermis is collenchyma. © BlueRidgeKitties CC by-nc-sa 2.0
A cross section of a pumpkin stem. The cellular layer located under the epidermis is collenchyma. © BlueRidgeKitties CC by-nc-sa 2.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



