-
 Puncture
Puncture
-
 Möbius strip
Möbius strip
-
 Key escrow
Key escrow
-
 Magnetometer
Magnetometer
-
 Specialised link
Specialised link
-
 Morphogenesis
Morphogenesis
-
 Cave
Cave
-
 Meningitis
Meningitis
-
 Neuroglia
Neuroglia
-
 Authorisation
Authorisation
-
 Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin
-
 Hapten
Hapten
-
 Constellation of Virgo
Constellation of Virgo
-
 Antidiabetic
Antidiabetic
-
 Syrian brown bear
Syrian brown bear
-
 Emulsion
Emulsion
-
 Chemoreceptor
Chemoreceptor
-
 Office automation
Office automation
-
 Decryption
Decryption
-
 Magnitude and intensity
Magnitude and intensity
-
 Prevalence
Prevalence
-
 Electrochemical cell
Electrochemical cell
-
 Anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory
-
 Melanoma
Melanoma
-
 H1 histamine antagonist antitussive
H1 histamine antagonist antitussive
-
 Hepatitis
Hepatitis
-
 Object-oriented language
Object-oriented language
-
 Biological corridor
Biological corridor
-
 Metabolic crossover
Metabolic crossover
-
 Heteroatom
Heteroatom
Spleen
The spleen is an immune system organ.
Function of the spleen
The spleen is a secondary lymphoid organ. In other words, it contributes to the immune response but is not involved in the synthesis or maturation of immune cells.
The spleen also plays a role in the maturation of red blood cells and in purifying blood by removing waste (degraded or unusable red cells, damaged platelets, viruses, and cell waste).
The spleen is also involved in the production of blood cells (hematopoiesis) in the foetus. In turn the liver and bone marrow then take on this role.
Structure of the spleen
The spleen is a soft organ measuring 12 cm x 8 cm x 4 cm on average, and weighing approximately 200 grams. This makes it the largest lymphoid organ in the human body. It is located in the abdominal cavity to the left of the stomach.
The spleen is covered by a very fragile connective tissue capsule. Inside, it is composed of two quite distinct parts.
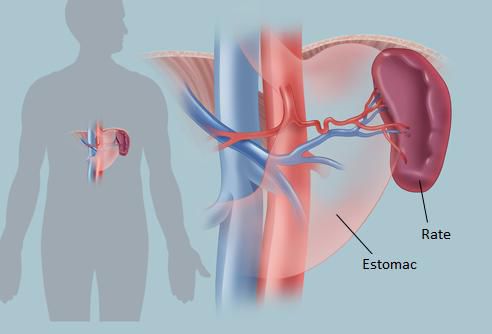 The spleen is a secondary lymphoid organ. © WebMD
The spleen is a secondary lymphoid organ. © WebMD
Latest
Fill out my online form.



