-
 Phenotype
Phenotype
-
 Carnivore
Carnivore
-
 Dense Plume
Dense Plume
-
 Intestinal absorption inhibitor
Intestinal absorption inhibitor
-
 Scalp
Scalp
-
 Juvenile water
Juvenile water
-
 Magma
Magma
-
 Lysosome
Lysosome
-
 Arthropyosis
Arthropyosis
-
 GMT
GMT
-
 Log in
Log in
-
 Spamming
Spamming
-
 Exothermicity
Exothermicity
-
 VLPO nucleus
VLPO nucleus
-
 Channelrhodopsin
Channelrhodopsin
-
 Anseriformes
Anseriformes
-
 Skype
Skype
-
 Ephemeris meridian
Ephemeris meridian
-
 Ferralisation
Ferralisation
-
 Kennedy Space Center
Kennedy Space Center
-
 CD-RW
CD-RW
-
 Breast-feeding
Breast-feeding
-
 Barebone computer
Barebone computer
-
 Halley's comet
Halley's comet
-
 Self-palpation
Self-palpation
-
 Synapse
Synapse
-
 Nucleotide
Nucleotide
-
 Formal language
Formal language
-
 Cardiovascular system
Cardiovascular system
-
 Duodenum
Duodenum
Peritoneum
Function of the peritoneum
The peritoneum is a think serous membrane that lines the deep surface of the abdomino-pelvic cavity and the organs contained in it. The organs located inside of the peritoneum are called "intraperitoneal" and the others are called " retroperitoneal" (often lying behind the peritoneum). Some organs are partly inside and partly outside of the peritoneum (pancreas).
Structure of the peritoneum
The peritoneum is formed from two superimposed layers known as sheets and is composed of a single layer of&nbsp:epithelial : cells
- the visceral peritoneum (which directly surrounds the organs) ;
- the parietal peritoneum (located on the wall of the abdominal cavity).
The two peritoneal sheets can move independently of each other.
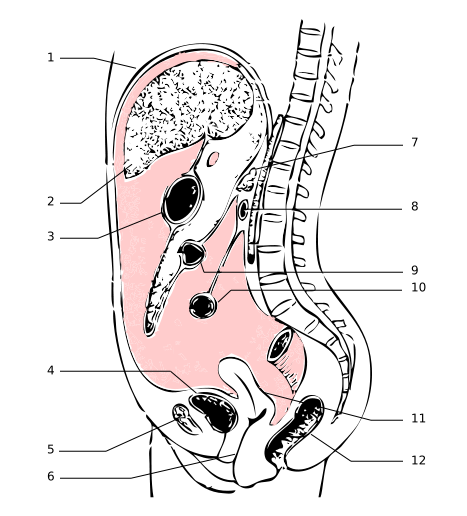 The peritoneum was a membrane which surrounds many organs. 1: diaphragm - 2 : liver - 3 : stomach - 4 : bladder- 5 : pubic bone - 6 : vagina - 7 : pancreas - 8 : duodenum - 9 : transverse colon - 10 : small intestine - 11 : uterus - 12 : rectum. © Wikimedia Commons
The peritoneum was a membrane which surrounds many organs. 1: diaphragm - 2 : liver - 3 : stomach - 4 : bladder- 5 : pubic bone - 6 : vagina - 7 : pancreas - 8 : duodenum - 9 : transverse colon - 10 : small intestine - 11 : uterus - 12 : rectum. © Wikimedia Commons
Latest
Fill out my online form.



