-
 Boreal forest
Boreal forest
-
 Discrete logarithm
Discrete logarithm
-
 Terrestrial time
Terrestrial time
-
 Schists
Schists
-
 Phenicol
Phenicol
-
 Simazine
Simazine
-
 YUV
YUV
-
 Viscoelasticity
Viscoelasticity
-
 Biological corridor
Biological corridor
-
 Spawning ground
Spawning ground
-
 Tertials
Tertials
-
 Pancreas
Pancreas
-
 Tritium breeding blanket
Tritium breeding blanket
-
 Mimicry
Mimicry
-
 Shipwreck of the Ievoli Sun
Shipwreck of the Ievoli Sun
-
 Serpentine
Serpentine
-
 ECMA
ECMA
-
 Single-flow CMV
Single-flow CMV
-
 Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
-
 Nail
Nail
-
 Poikilotherm
Poikilotherm
-
 Optical disk
Optical disk
-
 Anaphylactic shock
Anaphylactic shock
-
 Aulacogen
Aulacogen
-
 Truncation
Truncation
-
 Reptile
Reptile
-
 Active site
Active site
-
 Terrestrial planet
Terrestrial planet
-
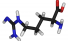 Arginine
Arginine
-
 Facilities management
Facilities management
Pancreas
The pancreas is part of the digestive system and the endocrine system.
Function of the pancreas
The pancreas is a mixed gland, as it is both exocrine and endocrine. Its main functions are to produce digestive enzymes in the digestive tract and to regulate blood glucose concentration.
1. Exocrine function
The pancreas produces pancreatic enzymes which are used by the digestive system, and empties them into the duodenum through the Wirsung duct. The proenzymes in pancreatic juice are inactive. They become active through the action of the gastric juice.
The enzymes which are activated are:
- proteases (trypsin, carboxypeptidase);
- ribonucleases (which degrade RNA);
- deoxyribonucleases (which degrade DNA);
- lipases (which degrade lipids);
- and amylases (which degrade starch).
Pancreatic juice has an alkaline pH, that neutralises the activity of chyme from the stomach.
2. Endocrine function of the pancreas
This is provided by the pancreatic islets of Langerhans, which are dispersed throughout the mass of the pancreas. The -α cells produce glucagon and the -β cells produce insulin, the two hormones involved in regulating blood glucose concentrations. Somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide are produced by the -δ and F cells of the islets respectively. Somatostatin regulates gallbladder secretion, increases the mobility of the intestine and inhibits the production of glucagon and insulin. Pancreatic polypeptide plays a role in the inhibition of exocrine pancreatic secretion.
Structure of the pancreas
The pancreas is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and in front of the kidneys. It is approximately 15 centimetres long and weighs 70 to 100 grams, making it the second largest gland in the human body after the liver. It has four parts: the head and isthmus that insert into the duodenum and the body and tail which extend to the spleen.
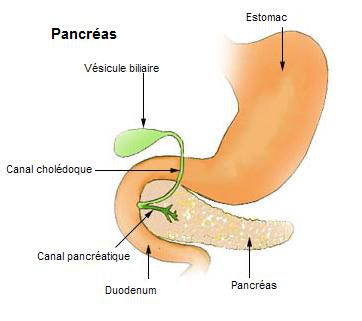 The pancreas empties pancreatic juice into the duodenum, and hormones directly into the blood. © DR
The pancreas empties pancreatic juice into the duodenum, and hormones directly into the blood. © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



