-
 Caucasian Elm
Caucasian Elm
-
 Muon neutrino
Muon neutrino
-
 Transfusion
Transfusion
-
 Viraemia
Viraemia
-
 Emollient
Emollient
-
 Computer network
Computer network
-
 Archaeopteryx
Archaeopteryx
-
 Fine particle
Fine particle
-
 Gas giant
Gas giant
-
 Radiative forcing
Radiative forcing
-
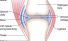 Joint
Joint
-
 Cellulose
Cellulose
-
 Freeware
Freeware
-
 Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis
-
 Cleavage
Cleavage
-
 Typosquatting
Typosquatting
-
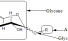 Oside
Oside
-
 Genus
Genus
-
 Plankton
Plankton
-
 JAXA
JAXA
-
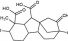 Gibberellins
Gibberellins
-
 SMS
SMS
-
 Fuel
Fuel
-
 Phenotype
Phenotype
-
 Depleted uranium
Depleted uranium
-
 Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis
-
 Peas
Peas
-
 Zeolite
Zeolite
-
 Planum
Planum
-
 Planet
Planet
Omega-3
The omega-3s are a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid whose first double bond - C=C is on the third carbon atom (starting from the side opposite the acid group).
The precursor of the omega-3s isα- linolenic acid, so other omega-3s can be produced from this fatty acid.
Linolenic α- acid is essential to our diet as the body cannot produce it. This omega-3 is found in oily fish, algae and in vegetable oils such as walnut oil, linseed oil and rapeseed oil.
The omega-3 are necessary for the correct functioning of the brain as they are involved in cell formation. They are also believed to be involved in reducing the risks of cardiovascular accidents.
Our body needs approximately 1 to 2 grams of omega -3 each day. On the other hand, excessive consumption is also harmful with an increase in bad cholesterol, fall in blood glucose and fluidification of the blood.
According to Afssa recommendations, omega-3s should be 1/5 of our omega-6 consumption although in general the ratio is far lower.
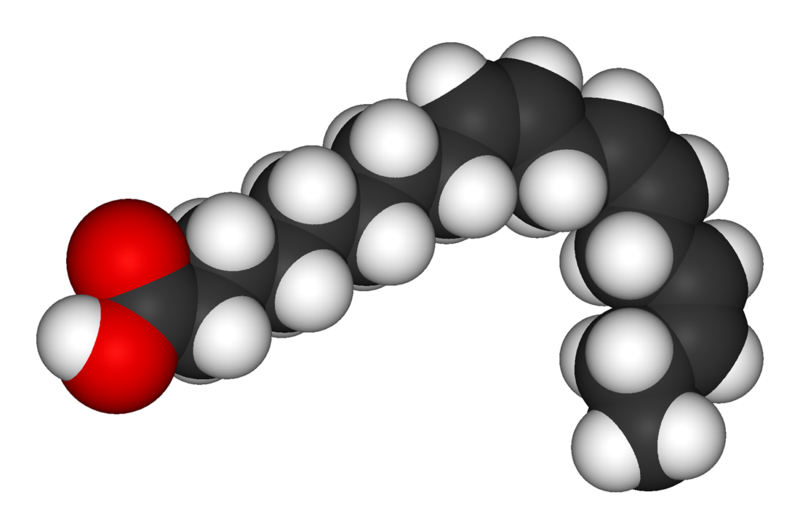 Linolenic acid is the precursor of omega-3. DR Credits
Linolenic acid is the precursor of omega-3. DR Credits
Latest
Fill out my online form.



