-
 Interferon
Interferon
-
 TPA
TPA
-
 Luminescence
Luminescence
-
 Ductility
Ductility
-
 Fan-coil unit
Fan-coil unit
-
 SALT
SALT
-
 Chrominance
Chrominance
-
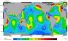 Amphidromic point
Amphidromic point
-
 Dorsum
Dorsum
-
 Brachiopod
Brachiopod
-
 SLAC
SLAC
-
 Spirit
Spirit
-
 SPICAV
SPICAV
-
 Möbius strip
Möbius strip
-
 Triple DES
Triple DES
-
 Temperate evergreen forest
Temperate evergreen forest
-
 Urushiol
Urushiol
-
 PET
PET
-
 Sea ice - Old ice
Sea ice - Old ice
-
 Constellation
Constellation
-
 Continental shelf
Continental shelf
-
 Gneiss
Gneiss
-
 Weak key
Weak key
-
 Creosote
Creosote
-
 Colposcopy
Colposcopy
-
 Desorption
Desorption
-
 Tidal bore
Tidal bore
-
 Water primrose
Water primrose
-
 Bird songs
Bird songs
-
 ELT
ELT
MicroRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) is composed of approximately twenty nucleotides, and is one of the main regulatory pathways for gene expression.
MicroRNAs are coded by the genome and then transcribed into a precursor in a handle and loop shape (like a tennis racquet). Enzymes cleave the RNA into a small single strand fragment of 21 to 24 nucleotides long.
Once they have matured this way the microRNA can regulate gene expression by binding to messenger RNAs carrying a homologous sequence. These are then damaged or their translation is inhibited.
The microRNAs have also been shown to be able to directly methylate DNA in order to switch off genes.
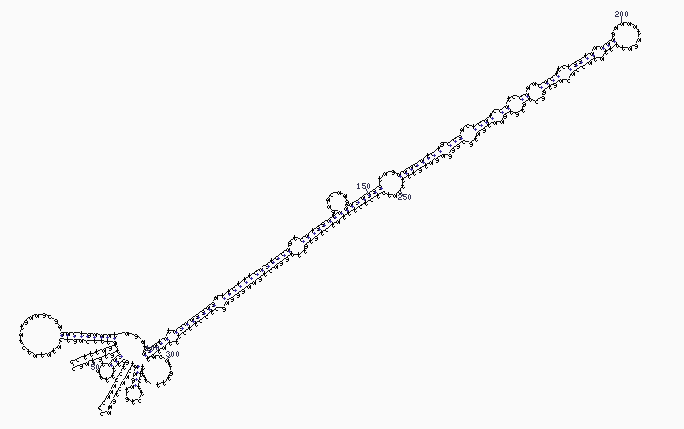 The microRNA precursors have a stem-loop structure. © Opabinia regalis /Licence Creative Commons
The microRNA precursors have a stem-loop structure. © Opabinia regalis /Licence Creative Commons
Latest
Fill out my online form.



