-
 Coastline Act
Coastline Act
-
 Big Crunch
Big Crunch
-
 Visual evoked potentials
Visual evoked potentials
-
 Faraday cage
Faraday cage
-
 Macula
Macula
-
 Amphihaline
Amphihaline
-
 Turkey oak
Turkey oak
-
 Abortion
Abortion
-
 Geotaxis
Geotaxis
-
 Capstone
Capstone
-
 Cilia
Cilia
-
 Myrmecologist
Myrmecologist
-
 Yellow dwarf
Yellow dwarf
-
 Aerocapture
Aerocapture
-
 Halogen
Halogen
-
 Robot
Robot
-
 Fistula
Fistula
-
 Nucleophile
Nucleophile
-
 Dietary supplement
Dietary supplement
-
 Alevin
Alevin
-
 Sonoluminescence
Sonoluminescence
-
 Gel-coat
Gel-coat
-
 Hardy kiwi
Hardy kiwi
-
 Dots per inch
Dots per inch
-
 Primaries (feathers)
Primaries (feathers)
-
 GPS
GPS
-
 Glottis
Glottis
-
 Bypass
Bypass
-
 Calcitonin
Calcitonin
-
 Aurora
Aurora
Lambda phage
The lambda phage is a model organism studied in biology laboratories.
Classification of the lambda phage
The lambda phage is a virus which belongs to the Siphoviridaefamily. It infects the bacterium which is widely used in the laboratory, Escherichia coli.
Characteristics of the lambda phage
The lambda phage has a 48,500 base pair, linear, double-stranded DNA genome which has been entirely sequenced. It has the typical shape of a bacteriophage, a head in which the DNA is encapsulated and a tail and fibrils which enable it to attach itself and insert its DNA into the cell.
It can be involved in two different cycles:
- the lytic cycle, in which the infected bacterium dies and releases a large number of new virions, synthesised as a result of expression of the viral genes, which particularly leads to the production of capsid proteins ;
- the lysogen cycle, in which the viral genome is incorporated into the bacterial genome (as a prophage) and where the latency genes are expressed.
Use of the lambda phage in the laboratory
The lambda phage is studied to improve our understanding of host-virus relationships and also as a cloning vector.
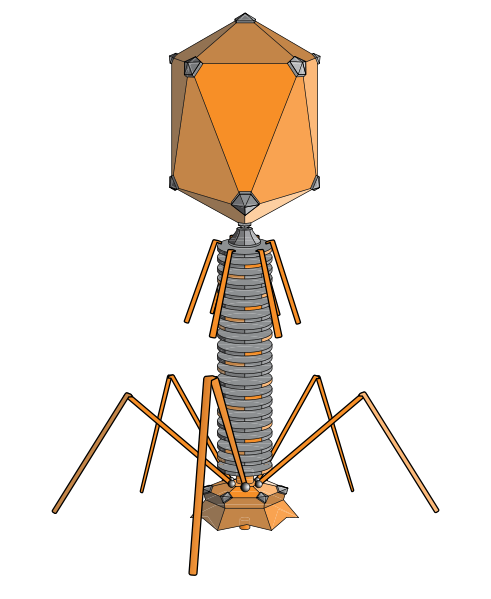 The lambda phage is a bacteriophage with a head, tail and fibrils. © adenosine, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
The lambda phage is a bacteriophage with a head, tail and fibrils. © adenosine, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



