-
 Full hybrid
Full hybrid
-
 A5
A5
-
 Orbiter
Orbiter
-
 Zune
Zune
-
 Anatomy
Anatomy
-
 Compressed air engine
Compressed air engine
-
 Staging
Staging
-
 Phases of the Moon
Phases of the Moon
-
 Brachiopod
Brachiopod
-
 SCART Connector
SCART Connector
-
 Nucleoside triphosphate
Nucleoside triphosphate
-
 Toluene
Toluene
-
 MOX fuel
MOX fuel
-
 C cells
C cells
-
 Alkalosis
Alkalosis
-
 Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia
-
 Milky Way
Milky Way
-
 Endeavour
Endeavour
-
 Endosome
Endosome
-
 Occiput
Occiput
-
 Insectivore
Insectivore
-
 ITU
ITU
-
 Nintendo DS
Nintendo DS
-
 Chalcogenide
Chalcogenide
-
 Conduction block
Conduction block
-
 Dry ice
Dry ice
-
 Cyclosilicates
Cyclosilicates
-
 Bit-map
Bit-map
-
 Haematology
Haematology
-
 Oberon
Oberon
Krebs cycle
The Krebs cycle (or de Szent-Györgyi and Krebs cycle, or yet again, the citric acid cycle) is a metabolic pathway which takes place in all cells in the cytoplasm of bacteria or in the mitochondria of eukaryotes.
Role of the Krebs cycle
The Krebs cycle plays a role in carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism but it is particularly known for enabling production of cellular energy in the form of the GTP de molecule. It produces one of these per cycle from a GDP molecule.
The molecules involved in the Krebs cycle
A molecule of citrate is gradually changed by enzymes in the presence of cofactors. There is a total of eight stages or eight molecules from the starting citrate to the final citrate:
- citrate ;
- isocitrate ;
- alpha-ketoglutarate ;
- succinyl CoA ;
- succinate ;
- fumarate ;
- malate ;
- oxaloacetate ;
- citrate.
Other molecules involved are acetyl-CoA, water, le carbon dioxide(CO2), NADH, le FADH2, and GTP etc.
Summary of the Krebs cycle
In total the Krebs cycle produces :
- 2 molecules of CO2 ;
- 3 molecules of NADH,H+ ;
- 1 molecule of CoQH2 ; and
- 1 molecule of GTP.
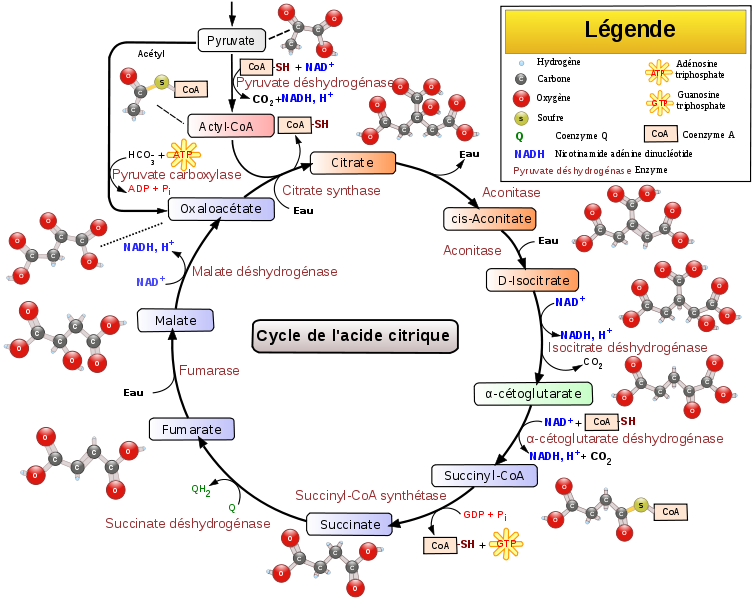 The Krebs cycle is a complex metabolic process. © Narayanese, WikiUserPedia, YassineMrabet, TotoBaggins, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
The Krebs cycle is a complex metabolic process. © Narayanese, WikiUserPedia, YassineMrabet, TotoBaggins, Wikimedia, CC by-sa 3.0
Latest
Fill out my online form.



