-
 RSA
RSA
-
 Broadband network
Broadband network
-
 Citrate cycle
Citrate cycle
-
 Autapomorphy
Autapomorphy
-
 Astronomical unit
Astronomical unit
-
 Spleen
Spleen
-
 Filtrate
Filtrate
-
 Phytophage
Phytophage
-
 Phreatic
Phreatic
-
 Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
-
 ESO
ESO
-
 Amphibolite
Amphibolite
-
 Luyten, Willem
Luyten, Willem
-
 Balm
Balm
-
 Lewis formula
Lewis formula
-
 Antibiotic sensitivity profile
Antibiotic sensitivity profile
-
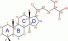 Steroid
Steroid
-
 Circadian
Circadian
-
 Layout planning
Layout planning
-
 Opt-in
Opt-in
-
 Metapopulation
Metapopulation
-
 PET
PET
-
 Oral contraceptive
Oral contraceptive
-
 Apoptosis
Apoptosis
-
 VLAN
VLAN
-
 Antisecretory H2 antagonist
Antisecretory H2 antagonist
-
 Wing fairing
Wing fairing
-
 Numéris
Numéris
-
 Locus
Locus
-
 Xerophile
Xerophile
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is a eukaryotic cellular organelle
Structure of the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is formed from a pile of small sacs (rather like a pile of plates). This pile is called the dictyosome, and is single in animal cells but multiple in plant cells. The cis face of the Golgi apparatus which is found before the endoplasmic reticulum is distinguished from the trans face which is turned towards the cytoplasm.
Role of the Golgi apparatus
The main role of the Golgi apparatus is to act as a site of transport and as a reservoir for proteins and lipids produced in the endoplasmic reticulum. The apparatus is part of the internal membrane which eukaryotic cells have produced so that macromolecules can be transported.
In particular, they enable post translational changes to be made to the newly produced proteins:
- glycosylation, or addition of sugar onto certain amino acids;
- cleavage of polypeptide precursors (division of peptides bonds)
- sulphation or addition of sulphate to certain amino acids;
- phosphorylation, or addition of phosphate.
These changes make the proteins functional.
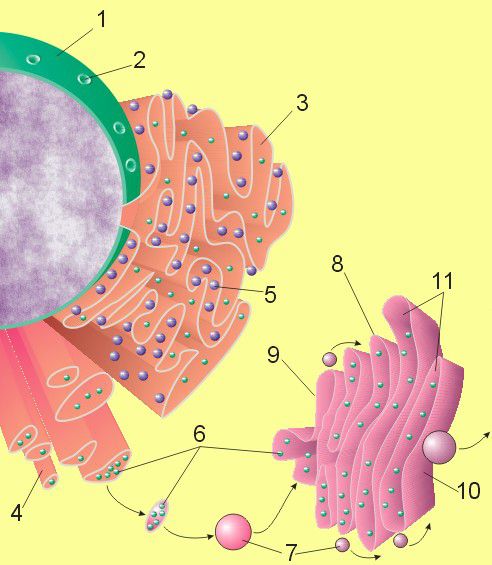 The Golgi apparatus is one of the organelles required to produce functional proteins. 1: nucleus; 2: nuclear pore ; 3: granular endoplasmic reticulum (GER); 4: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) ; 5: ribosome on the RER ; 6: transported proteins; 7: transport vesicle; 8: Golgi apparatus; 9: cis face of the Golgi apparatus ; 10: trans face of the Golgi apparatus ; 11: Golgi apparatus saccule. © Magnus Manske, Wikimedia, public domain
The Golgi apparatus is one of the organelles required to produce functional proteins. 1: nucleus; 2: nuclear pore ; 3: granular endoplasmic reticulum (GER); 4: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) ; 5: ribosome on the RER ; 6: transported proteins; 7: transport vesicle; 8: Golgi apparatus; 9: cis face of the Golgi apparatus ; 10: trans face of the Golgi apparatus ; 11: Golgi apparatus saccule. © Magnus Manske, Wikimedia, public domain
Latest
Fill out my online form.



