-
 Interambulacrum
Interambulacrum
-
 Black mulberry
Black mulberry
-
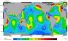 Amphidromic point
Amphidromic point
-
 Batrachians
Batrachians
-
 Empirical formula
Empirical formula
-
 Tropical period
Tropical period
-
 Invasive
Invasive
-
 Hovering
Hovering
-
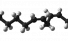 Linoleic acid
Linoleic acid
-
 Acid
Acid
-
 Heat transfer fluid
Heat transfer fluid
-
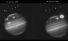 Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet
Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet
-
 Simazine
Simazine
-
 Lazarus taxon
Lazarus taxon
-
 Secondary
Secondary
-
 Intravenous
Intravenous
-
 Defecation
Defecation
-
 Miocene
Miocene
-
 Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen cycle
-
 Blazar
Blazar
-
 Diaphragm
Diaphragm
-
 Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides
-
 Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
-
 Tomography
Tomography
-
 Biotic crisis
Biotic crisis
-
 Black liquor
Black liquor
-
 Intumescent
Intumescent
-
 HD-DVD
HD-DVD
-
 Audiotex
Audiotex
-
 Arteriole
Arteriole
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is the skeleton of the cell.
Structure of the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a filamentous network within a cell giving it its mechanical properties. It contains many types of filaments in eukaryotes:
- flexible polymerised actin filaments and ;
- small, so-called intermediary filaments (the role of which is poorly understood) ;
- rigid microtubules .
Function of the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton provides the cell with a degree of rigidity and is used to fix the organelles (the equivalent to the cell as the organs in the body).
The cytoskeleton reorganises itself continuously and therefore controls internal movements (for example movement of chromosomes) and deformations of the membrane (production of protuberances, invaginations and adhesion sites, etc.)
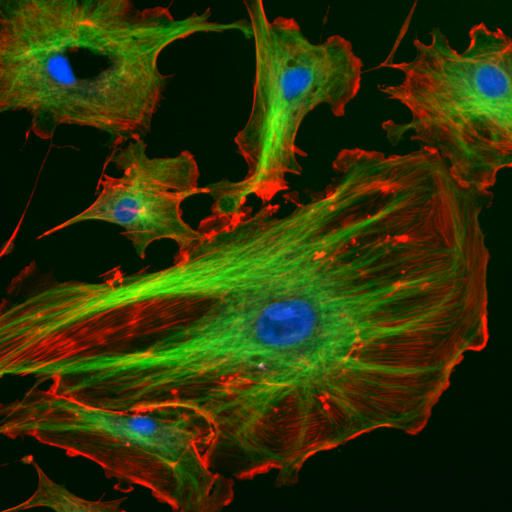 The parts of the cytoskeleton can be labelled with fluorescent proteins. Here, actin is shown in red and the microtubules in green (and the nucleus in blue). © DR
The parts of the cytoskeleton can be labelled with fluorescent proteins. Here, actin is shown in red and the microtubules in green (and the nucleus in blue). © DR
Latest
Fill out my online form.



